Model Of An Atom Including All Subatomic Particles
Elementary charge of an electron is the `-1.(40)*10^-19` coulombs.
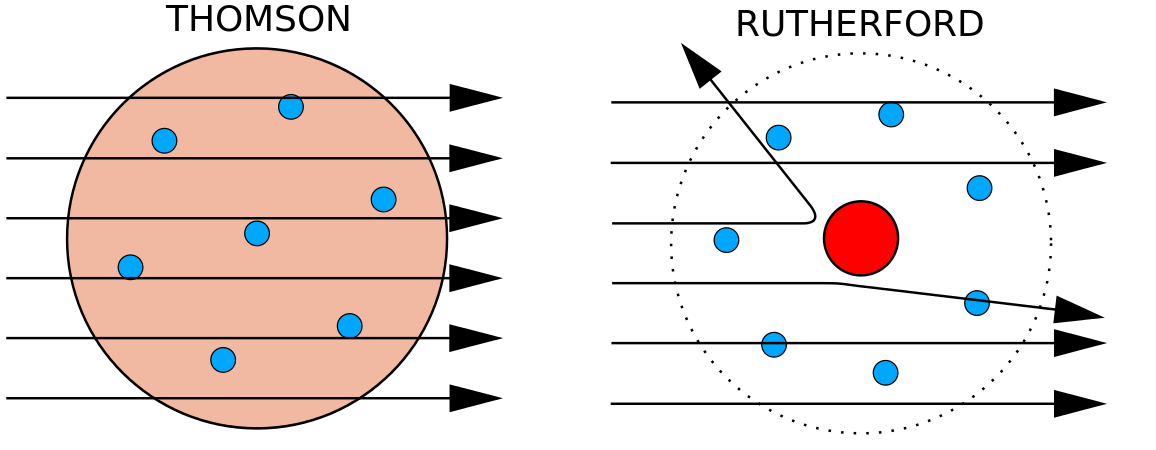
Model of an atom including all subatomic particles. Rutherford model, also called Rutherford atomic model, nuclear atom, or planetary model of the atom, description of the structure of atoms proposed (1911) by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. I can define an ion and determine its charge by the subatomic particles. Proposed the Modern Electron Cloud Model of the atom.
The three subatomic particles determine the overall charge of an atom, the chemical characteristics it can possess and its physical properties. Later, the scientists discovered particles inside the atom that proved, the atoms are divisible. Properties of subatomic particles electrons An electron is an elementary particle, that is, it is an indivisible subatomic particle, as it possesses no sub-components.
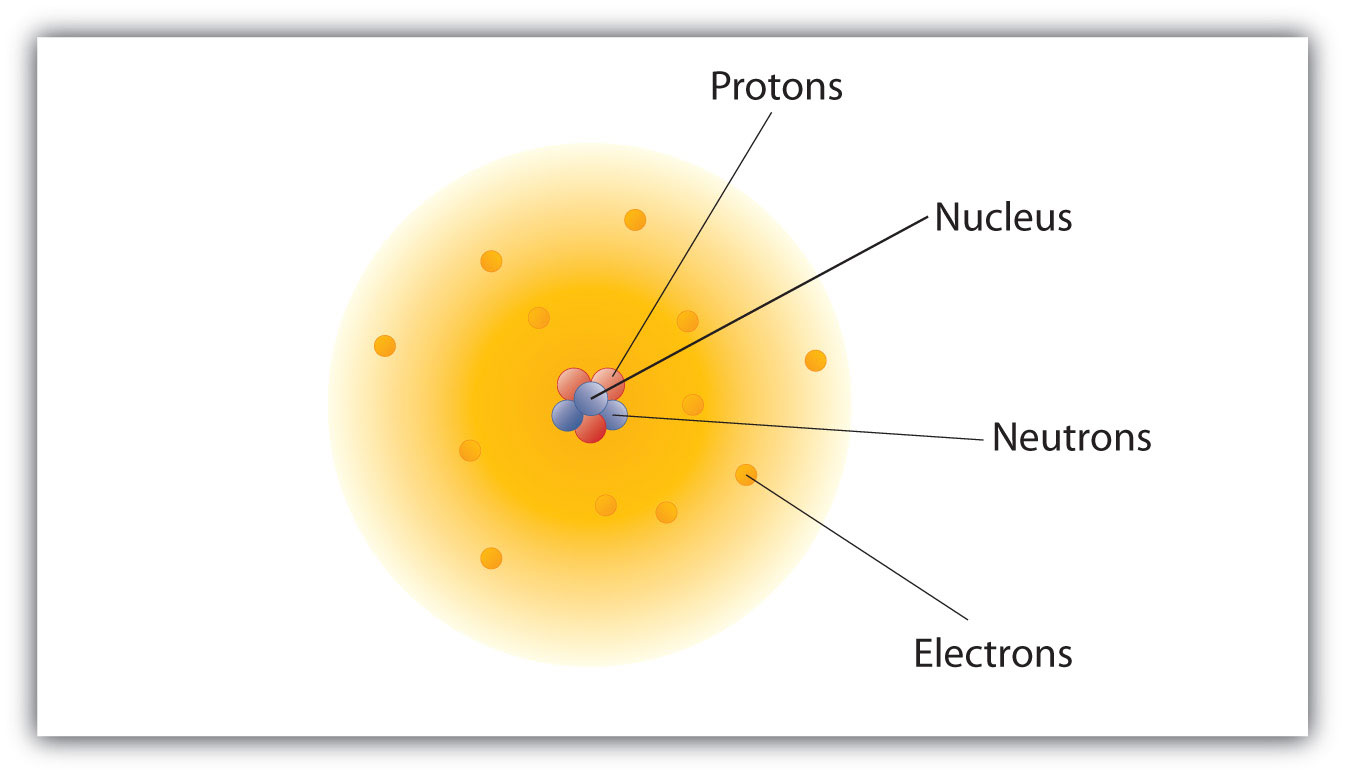
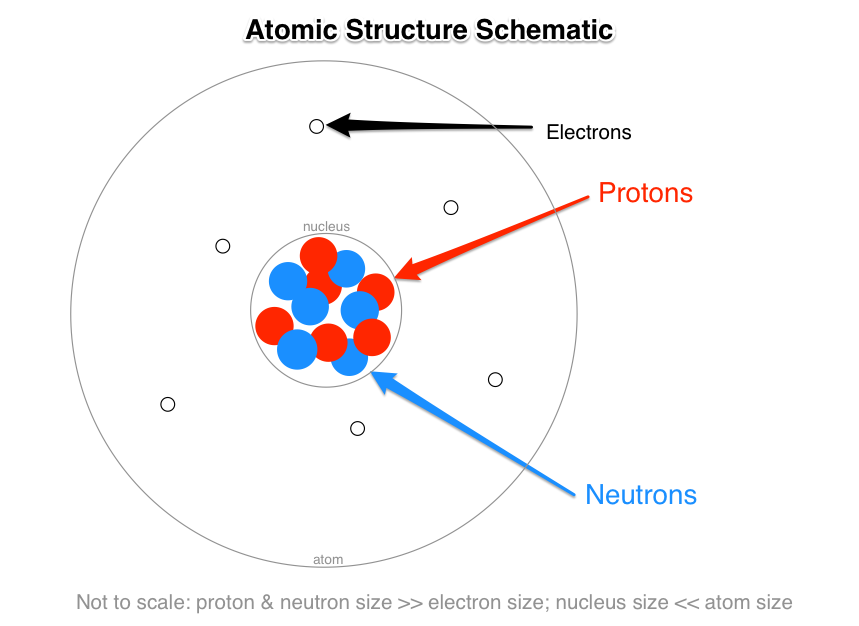
The center of the atom is called the nucleus. It cannot be broken down or sectioned. Nucleons include protons and neutrons.
Protons are positively charged and are found in the nucleus, deep in the centre of the atom. Atomic Theory & Atomic. The magnitude of the positive charge in the nucleus of every atom of a particular element is the same.In other words, all atoms of the same element have the same number of protons.
Subatomic particles Subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than an atom. HOW BIG IS THE NUCLEUS OF AN ATOM?. But in the latter part of the 19th century and early part of the th, scientists discovered that atoms are composed of certain subatomic particles and that, no matter what the element, the same subatomic particles make up the.
I can calculate subatomic particles from a Chemical symbol or write a Chemical symbol from subatomic particles. The number of subatomic particles, protons, neutrons, and electrons,…. All protons are identical.
But all of a sudden when you're dealing with an atom, reflected light you could almost view it as too big, or too blunt of an instrument with which to observe an atom. The Bohr model shows the three basic subatomic particles in a simple manner. A solid nucleus around which electrons orbit like tiny planets.
Properties of these subatomic particles. There are many subatomic particles including quarks, leptons, hadrons, bosons, and hadrons just to name a few. Most of an atom's mass is in the nucleus—a small, dense area at the center of every atom, composed of nucleons.
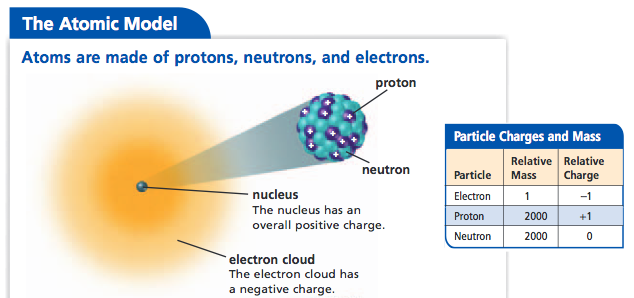
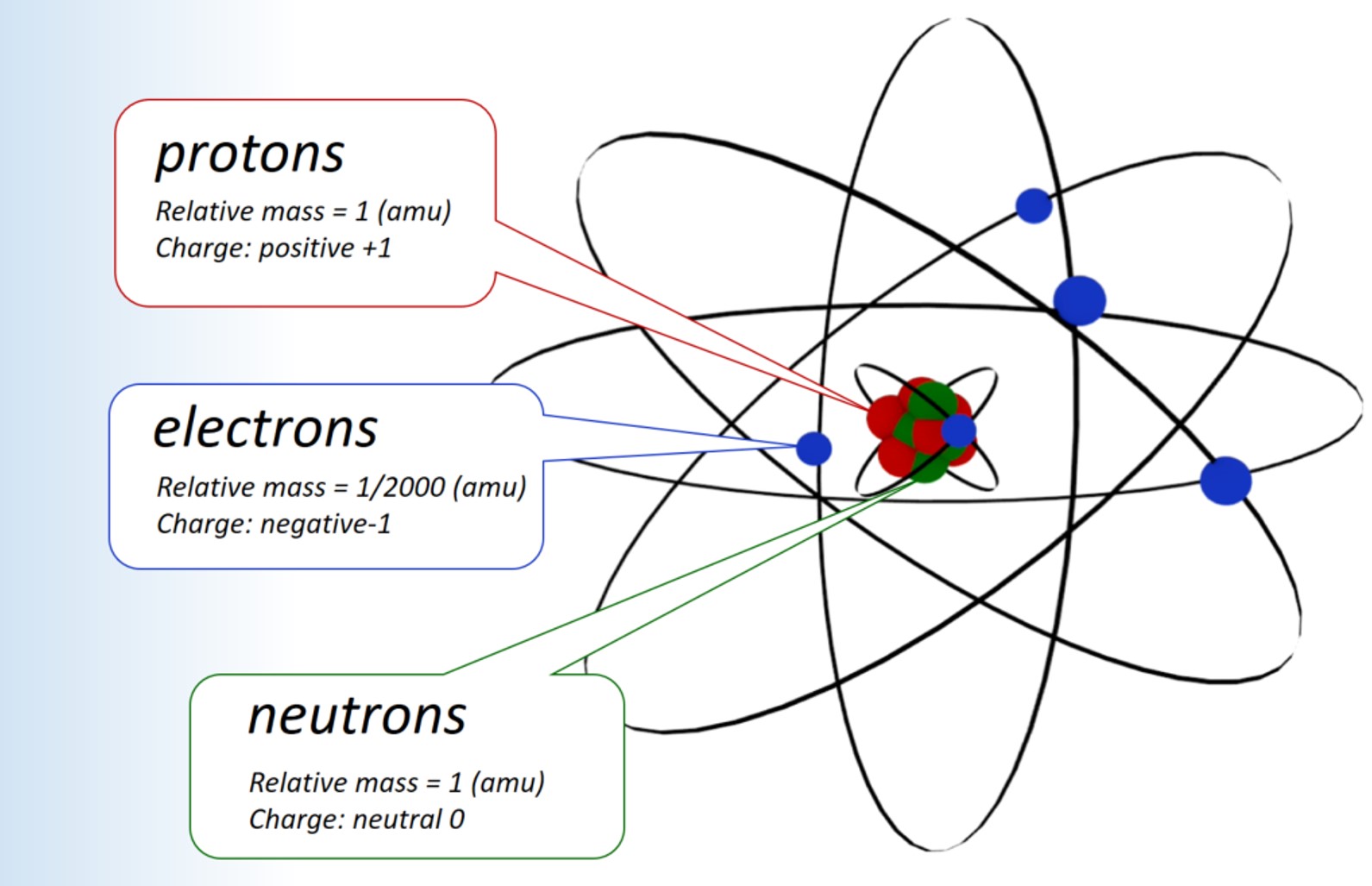
In 1940, the number of subatomic particles known to science could be counted on the fingers of one hand:. Protons have a positive (+) charge. The three main subatomic particles that form an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
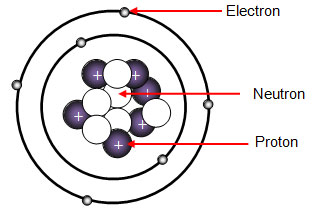
The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). The Bohr model of an atom was able to explain the stability of the atom and also could explain the phenomenon of atomic spectra and ionization of gases. I can define an isotope and determine its atomic mass by the subatomic particles.
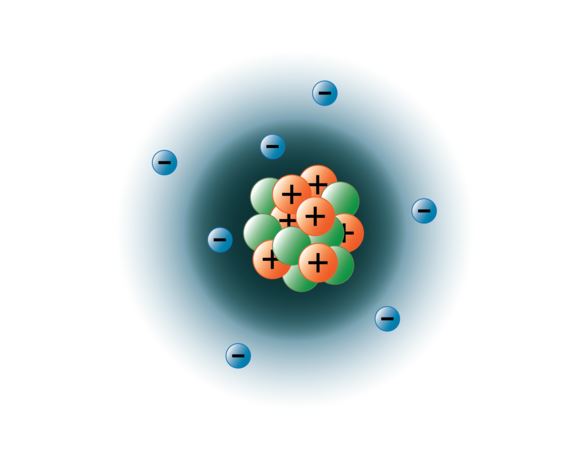
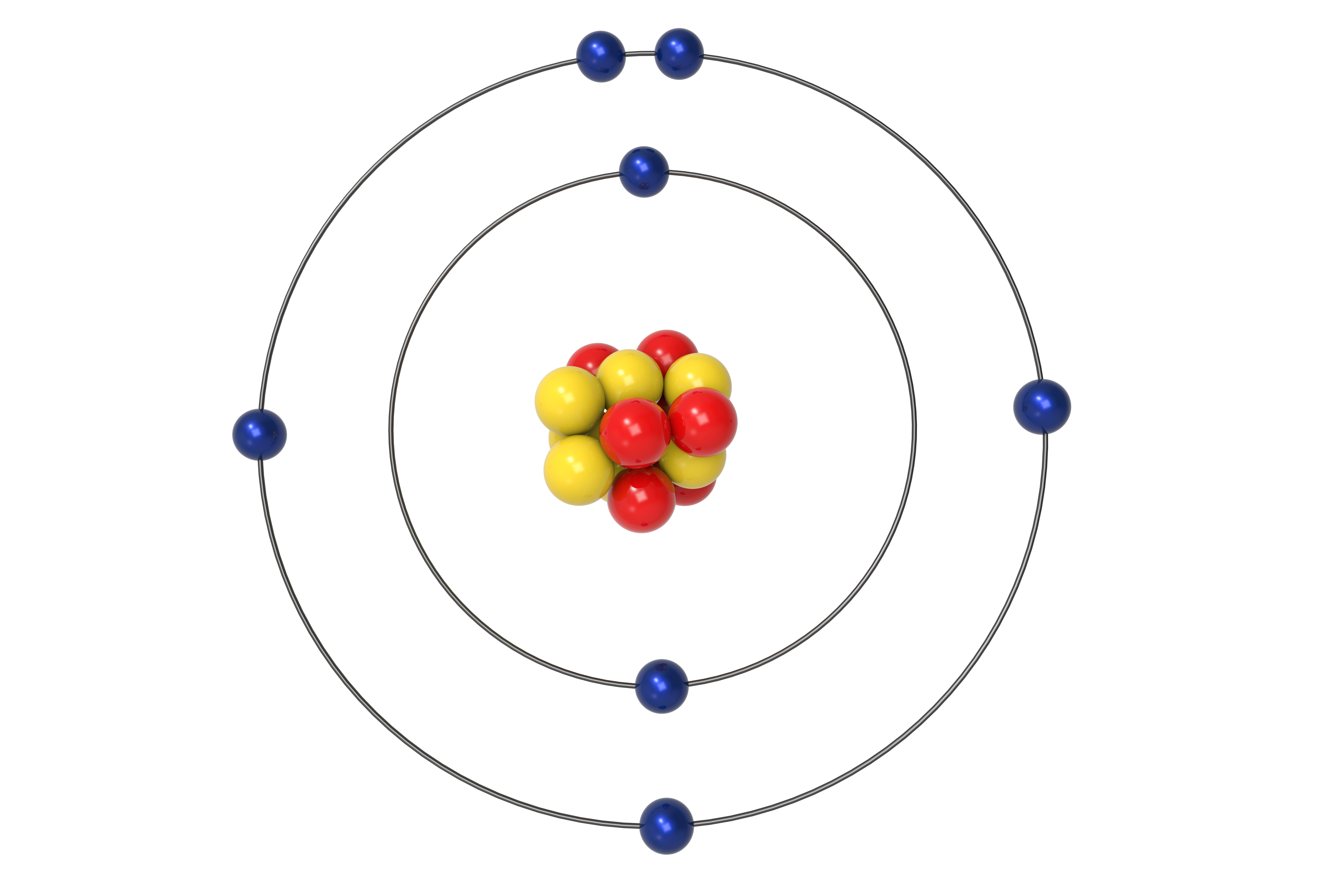
Anyway, this is a depiction of a helium atom. * An atom consists of a nucleus, which has positive electric charge, surrounded by a cloud of electr. Which subatomic particles are charged?.
They are particles that are smaller than an atom. The three main subatomic particles of an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. First, let's learn a bit about protons and neutrons, and then we will talk about electrons a little later.
The word 'atom' comes from the Greek word 'a-tomio' which means 'uncuttable' or 'non-divisible'. NAME and DESCRIBE the three subatomic particles. Atom of one element have properties that differ from properties of other elements.
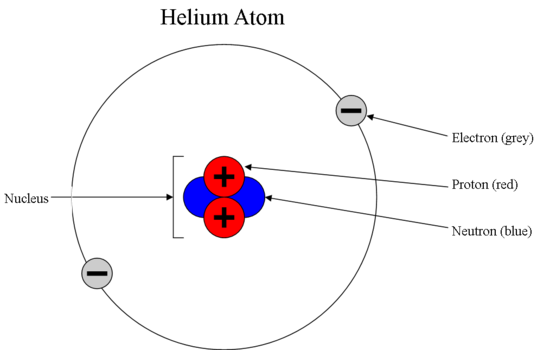
Protons, neutrons and electrons make up the subatomic particles of an atom. Subatomic particles with a negative charge Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Protons, neutrons, and electrons (as seen in the helium atom below).
They can be composite particles, such as the neutron and proton;. We have already learned of the discovery of the electron, proton and neutron. An atomic model cannot be used to represent the relative number of each subatomic particle within a specific atom.
A) Protons and neutrons b) Electrons c) Neutrons d) Protons 2) The electron can be found in what location of an atom?. Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus of an atom. The three main sub-atomic particles that determine the structure of the atom are protons, neutrons and electrons.
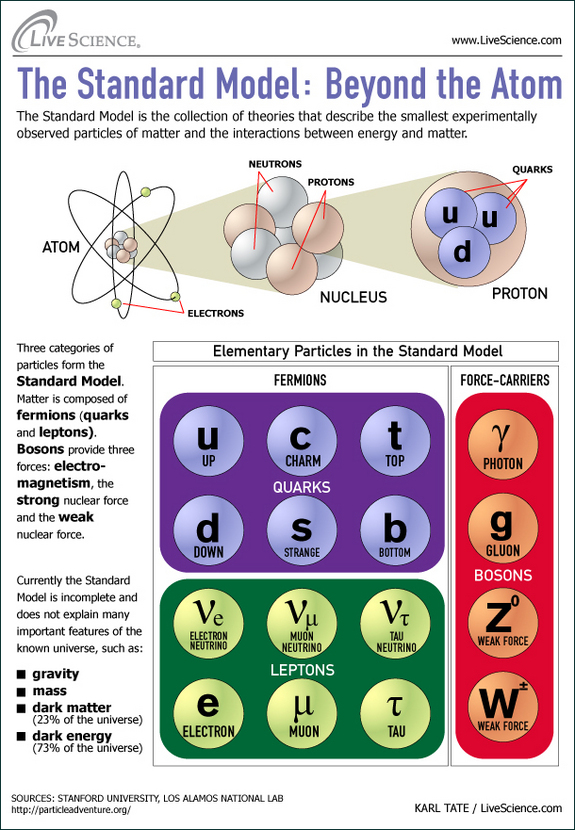
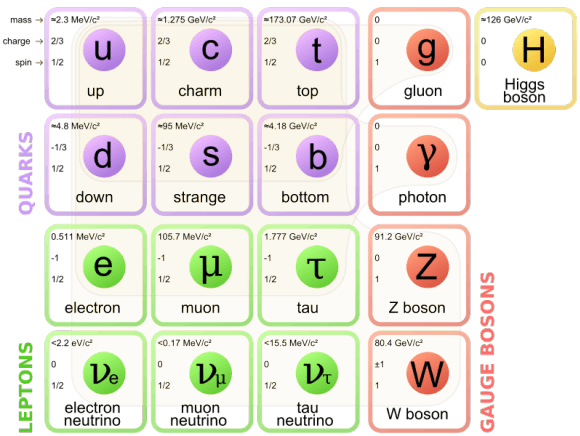
General Physics This is a list of particles in particle physics, including currently known and hypothetical elementary particles, as well as the composite particles that can be built up from them. The current understanding of the state of particle physics is integrated within a conceptual framework known as the Standard Model. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms.
Since 1932, through continued experimentation, many additional particles have been discovered in the atom. Elementary particles from the Standard Model of particle physics that have so far been observed. Democritus, a Greek who lived from 460 BCE to 370 B.C., developed a new theory of matter;.
1) What subatomic particles are located in the nucleus and have no effect on the charge of the atom?. During the 1910's, experiments with x- rays led to this useful conclusion:. Therefore, scientists set out to design a model of what they believed the atom could look like.
However, in the early th century, some scientists showed that atoms can be further divided into smaller parts called as the sub-atomic particles. There are three scaffolded difficulty levels. These are the what give each atom its unique characteristics.
Describe the structure of the atom including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud. 07 Schools Wikipedia Selection.Related subjects:. List the charge, mass, and location of each of the three subatomic particles found within atoms.
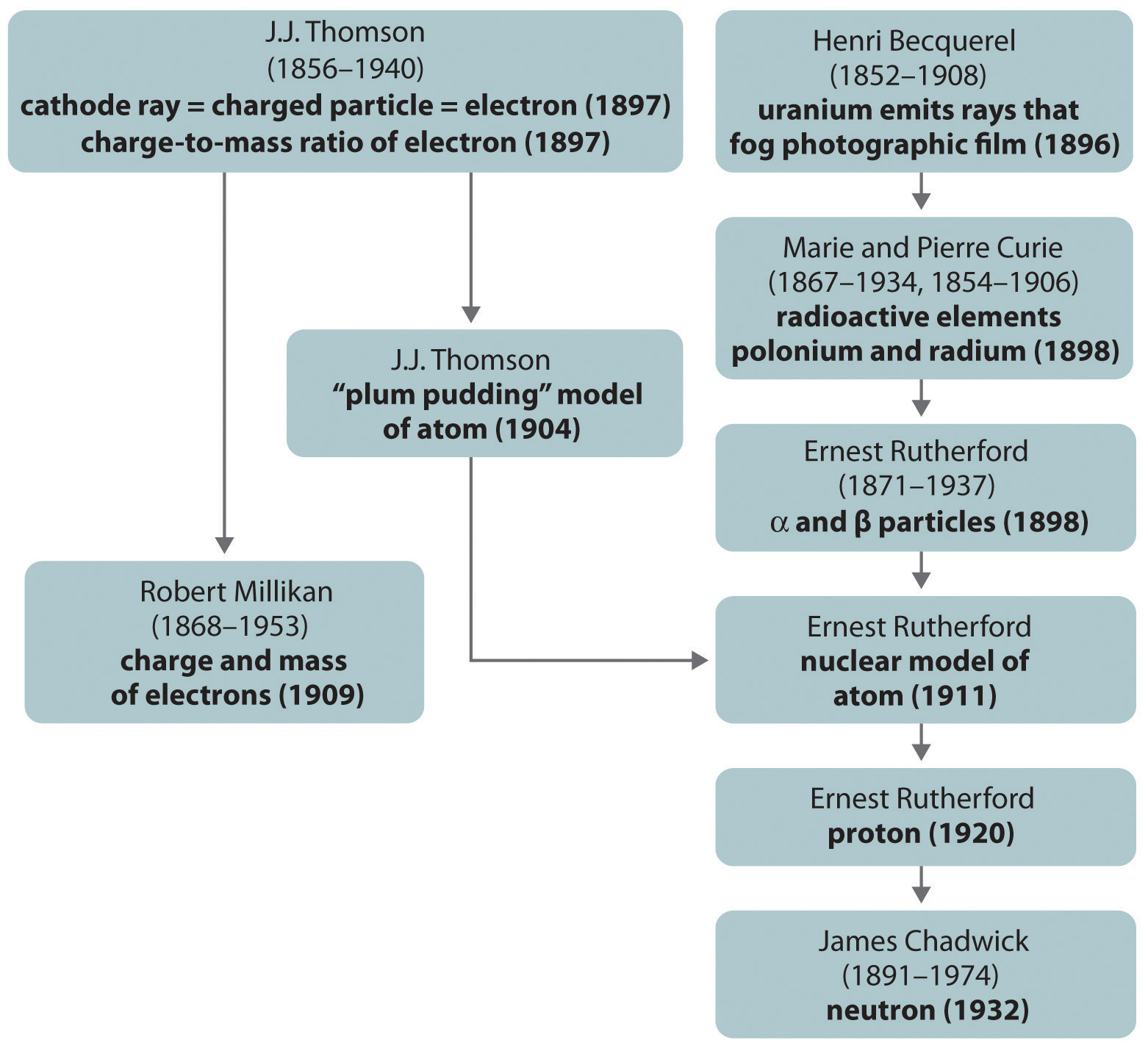
One tiny change makes a big difference and changes the identity of the atom. The atom is the smallest unit on Earth. An instructor explains nature of a cathode ray tube and the discovery of the electron.
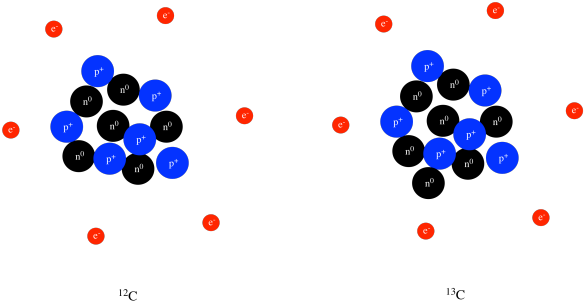
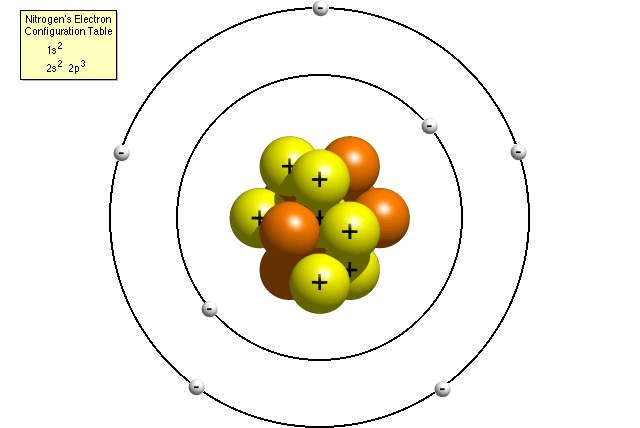
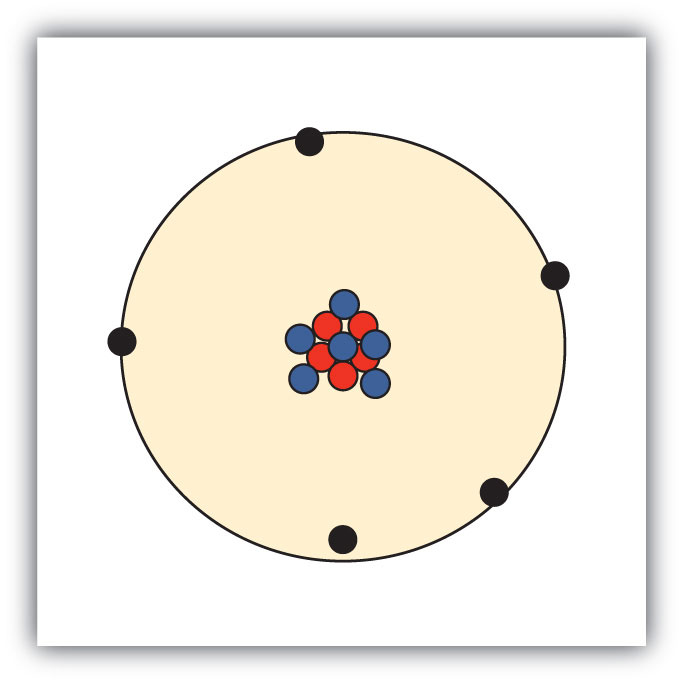
The diagram shows a model of a carbon atom, with an atomic INK VISUALLY number of 6. An electron is negatively charged. Subatomic Particles The Subatomic Particles Concept Builder challenges learners to use information regarding the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom in order to complete a table showing such data for a variety of isotopes.
The discovery of various subatomic particles is as follows:. A helium atom has two protons and two neutrons. Or at least this helium atom has two protons and two neutrons.
Electrons are among the (most, least) massive subatomic particles, and they are found (inside, outside) the nucleus. With the discovery of the neutron, an adequate model of the atom became available to chemists. Protons and Neutrons Describe Rutherford's model of the atom, including the location of protons, neutrons, and electrons with respect to the nucleus.
When the principles of quantum mechanics were developed, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle , discovered by German physicist Werner Heisenberg (1901–1976) meant the Bohr atom had to be modified. The discovery of particles inside atoms led to a better understanding of chemical species, these particles inside the atoms are called subatomic particles. The total volume of an atom is about a trillion times the volume of its nucleus.
Or elementary particles, which according to the standard model are not made of other particles. The model includes only the fundamental particles in the Table above. The numbers of particles in an atom can be calculated from its atomic number and mass number.
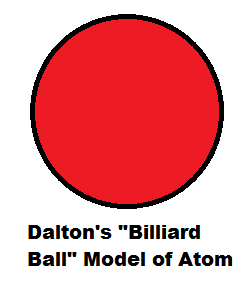
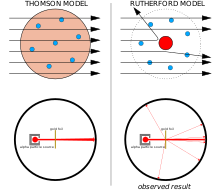
Describe why Rutherford used the term planetary modelto describe his model of atomic structure. For quite a while, the atom was thought to be the smallest part of matter that could exist. Billiard Ball Model Raisin Bun Model Beehive Model.
A typical atom consists of three subatomic particles:. What limitations might an atomic model have in properly illustrating the structure of an atom?. Other subatomic particles include Leptons, which combine with Fermions to form the building blocks of matter.
Though known to have serious defects, the Bohr model still supplies the standard graphic representation of the atom:. Look it up now!. It is also represented using the symbol -e.….
For a chronological listing of subatomic particles by discovery date, see Timeline of particle discoveries. This is a difficult task because of the incredibly small size of the atom. An atomic model.
Describe the structure of an atom, including the subatomic particles, their charges, and location.-Subatomic Particles:. Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. Schrödinger solved a series of mathematical equations to to come up with a model for the distributions of electrons in an atom.
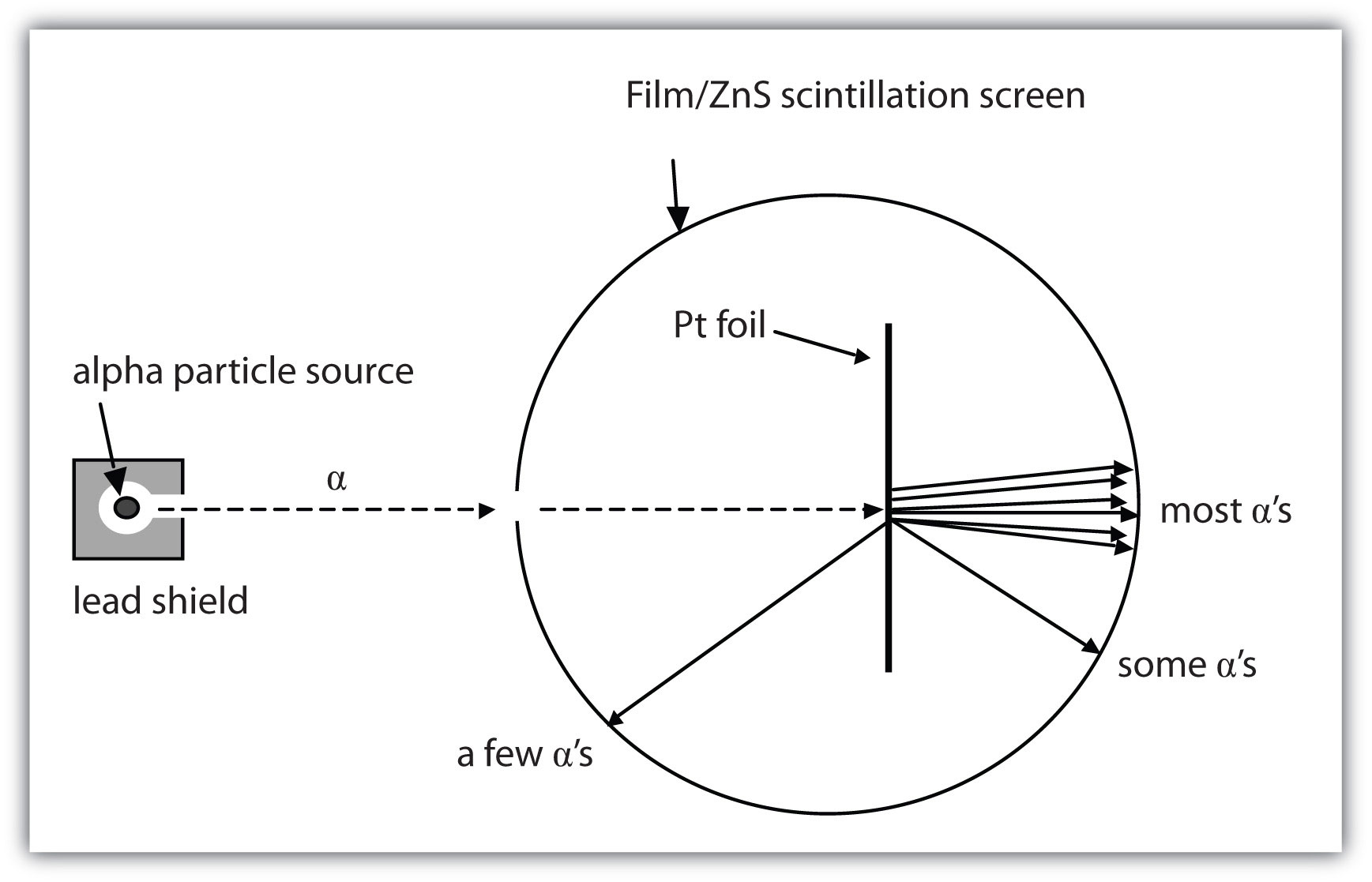
Model of the Atom An atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. Mass and positive charge in the gold atoms is concentrated in a small area. Most of the atom is empty space.
Also, new elements have been created by bombarding existing nuclei with various subatomic particles. James Chadwick and Discovery of Neutrons There were a lot of problems related to the calculation of the mass of the nucleus, although Rutherford’s model could explain the scattering of alpha problem. Protons are among the (most, least) massive subatomic particles, and they are found (inside, outside) the nucleus.
Elements and Isotopes The diagrams show models of carbon isotopes. Based on their knowledge of subatomic particles, scientists have developed a theory called the standard model to explain all the matter in the universe and how it is held together. Subatomic particles are particles that are smaller than the atom.
The atomic model consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in shells. Subatomic particles are the things that make up an atom. In the physical sciences, subatomic particles are smaller than atoms.
The atom is the smallest particle of matter than cannot be divided using a chemical means, but atoms consist of smaller pieces, called subatomic particles. Play this game to review Periodic Table. Other particles exist as well, such as alpha and beta particles (which are discussed below).
All atoms of one element have the same properties. Scientists believed that atoms were indivisible for the longest time. The subatomic particles called protons and neutrons are located within the nucleus of an atom.
Protons, neutrons, electrons, neutrinos, and positrons. 9.Explain an atom’s energy levels and orbitals which contain electrons.-8 is the lucky number-(1) orbital can only contain (2) electrons 10. The next step after the discovery of subatomic particles was to figure out how these particles were arranged in the atom.
This elementary charge is regarded as a physical constant. His atomic model was solid, and stated all atoms differ in size, shape, mass, position and arrangement, with a void exists between them. Breaking it down even further, the subatomic particles often consist of elementary particles.
Subatomic particles are to atoms what nitrogenous bases are to DNA. Particle physics and nuclear physics study these particles and how they interact. Identify that protons determine an element's identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity.
I can draw a Bohr & e-dot model of an element. According to Rutherford's model, all of an atom's positive charge is concentrated in its nucleus. Protons, neutrons, and electrons are the three main subatomic particles found in an atom.
Explain how the distribution of electrons in an atom or ion determines its behavior. Neutrons are similar to protons in size and mass, but they do not carry any charge (they are neutral). There are six leptons in the present atomic model:.
Subatomic particles include electrons, negatively charged, nearly massless particles that account for much of the atom’s bulk, that include the stronger building blocks of the atom’s compact yet very dense nucleus, the protons that are positively charged, and the strong neutrons that are electrically neutral. All Standard Model particles including the Higgs boson have been verified, and all other observed particles are combinations of two or more Standard Model particles. There are subatomic particles within an atom.
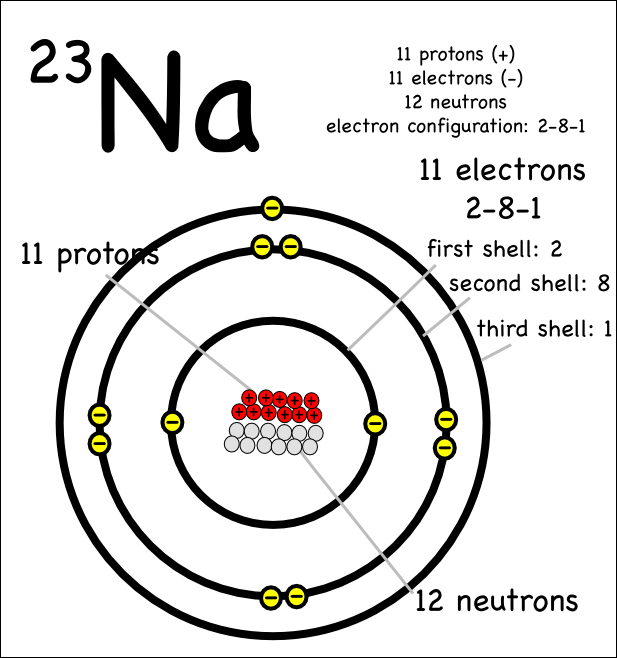
Subatomic particles are particles that are located inside of atoms. The numbers of subatomic particles in an atom can be calculated from its atomic number and mass number. Consider a neutral atom with 30 protons and 34 neutrons.
It is the basic component of any type of matter. His ideas were based on reasoning rather than science, and drew on the teachings of two Greek. The Standard Model is the most comprehensive existing model of particle behavior.
The electron, muon, and tau. Hi, you asked “What are sub-atomic particles made of?” “Subatomic particles” means “things smaller than an atom, of which atoms are composed”. No other particles are needed to explain all kinds of matter.
Label all particles and the nucleus. Subatomic particles with a negative charge. His model shows the nucleus surrounding by clouds of electron density.
Properties of Subatomic Particles Particle Symbol Relative charge Relative mass (mass of proton = 1) Actual mass (g) Electron e– 1– 1/1840 9.11 10–28 Proton +p 241+ 1 1.67 10– Neutron 0n 0 1 1.67 10–24 Interpret Data. Mats Persson / Getty Images. The atom is the smallest part of matter that represents a particular element.
Atomic Theory

Atomic Theory Ppt Download

What Is A Subatomic Particle Definition Mass Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Model Of An Atom Including All Subatomic Particles のギャラリー
Simple Science Particles

Sub Atomic Particles Chemistry Libretexts

Q Tbn 3aand9gcqx0q13d2srx38t9bdplhd3vqk Eboyxg7ldq Usqp Cau
Structure Reactivity Atoms Protons Neutrons Electrons

Sub Atomic Particles Atoms Siyavula

Atomic Models Learn Chemistry Class 9 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network

5 Atom Models Atom Models Bohr Chemistry En Nuclear Plum Pudding Science Solid Sphere Wave Mechanical Glogster Edu Interactive Multimedia Posters

Quarks Up Quarks Down Quarks Structure Of Proton Neutron Mass Charge Gcse Physics Ks4 Science Igcse Gce A Level Chemistry Physics Revision Notes
Atomic Models Wikilectures

Subatomic Particle Definition Examples Classes Britannica
What Are The Parts Of An Atom
3 3 Subatomic Particles Electrons Protons And Neutrons Chemistry Libretexts
Questions And Answers How Do I Make A Model Of An Atom

Atomic Structure And Subatomic Particles Youtube
Www Sisd Net Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 1297 The History Of The Atom Notes Condensed Pdf

Atomic Structure Electrons Protons Neutrons And Atomic Models

Atomic Structure And Subatomic Particles Youtube
Modern Quantum Model Schrodinger And Chadwick The History Of The Atom

2 Atomic Models School Of Materials Science And Engineering
Atomic Theory

Dalton S Atomic Theory Postulates Limitations Concepts Videos Q A

Elements And Atoms The Building Blocks Of Matter Anatomy And Physiology I

Subatomic Particles Atomic Model Project123
Atom Wikipedia
Matter And Energy Atomic Structure Texas Gateway
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqgjkrd5gkmnigetf33u84ysqh290ib5dpweh5oge Qxwwxtmvv Usqp Cau

Chapter 4 Atomic Theory Matter Matter All Matter Is Made Of Atoms O Alone As Elements Au Na O He O In Combination Of Elements As Compounds H 2 O Ppt Download
The Structure Of Atoms

History Of The Atom Ck 12 Foundation

M M Model Of The Atom Edible Subatomic Particles Howtosmile

Ncert Solutions Structure Of The Atom Chemistry Class 9
Drawing Atoms Montessori Muddle

Atom Diagram Universe Today

Ch 3 Atomic Structure Subatomic Particles Ppt Download

Can We Believe The Solar System Is Like The Atomic Model And May Be As Small As An Atom Relatively When I Look At The Solar System It Looks Like An Atom

The Atom Chemistry Is My Jam Atom Electron Configuration Atomic Theory

Rutherford Atomic Model Observations And Limitations In Detail

Atomic Structure Nucleus Proton Neutron Electron Mass Charge Isotopes Electron Arrangement Rutherford Bohr Model Of Atom Allotropes History Of Atomic Structure Model Development Ionisation Ions Gcse Chemistry Revision Notes Quizzes Ks4 Science

Particle Physics Wikipedia

The Structure Of Atoms

Subatomic Particles

Atomic Theory Tor Hertzog S Collection Of 30 Physics Ideas In
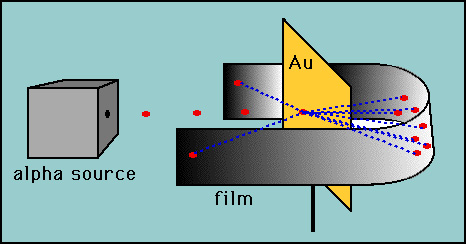
Rutherford Model Of The Atom

Rutherford Model Of The Atom Definition Diagram Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
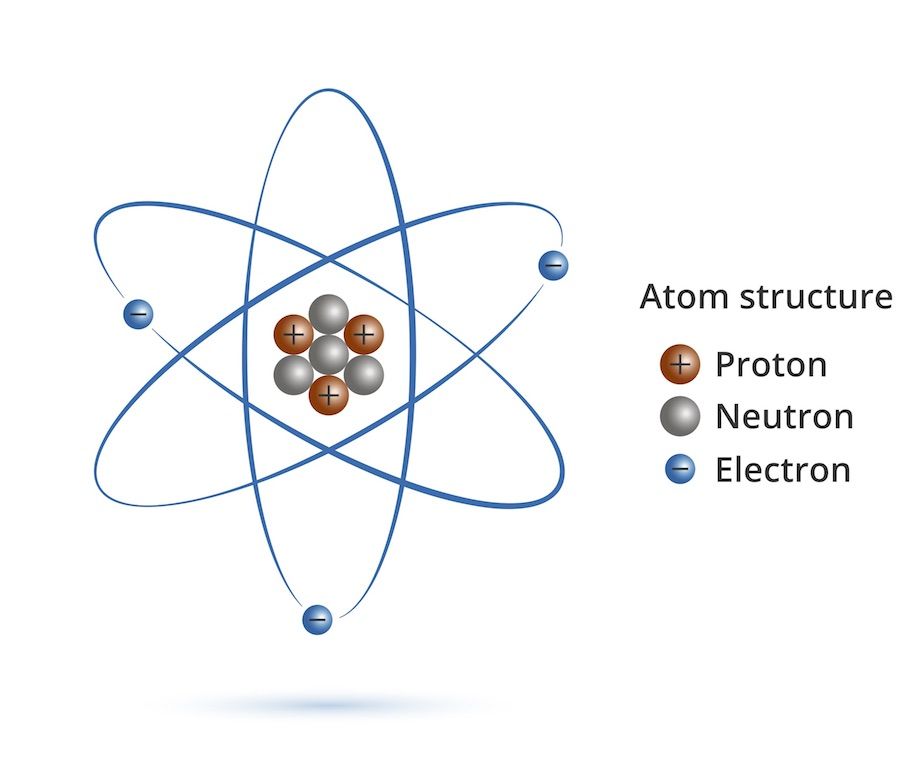
What Is An Atom Live Science
3
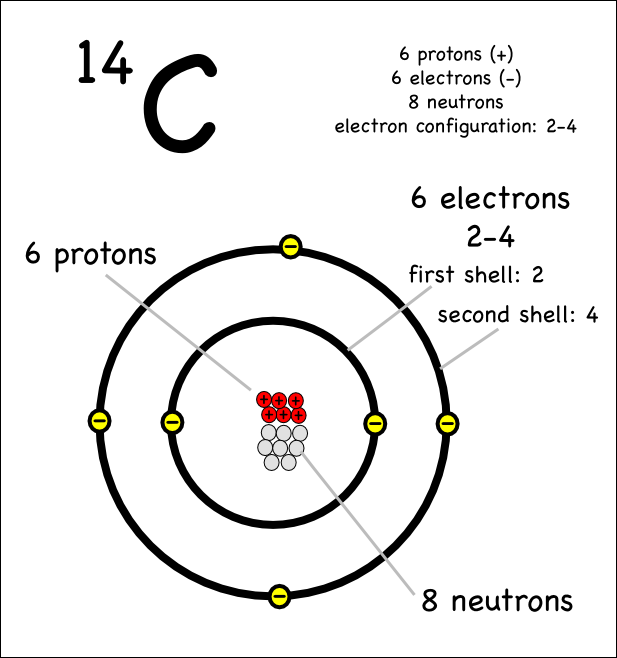
Drawing Atoms Montessori Muddle

The Structure Of The Atom Boundless Chemistry

Subatomic Particles

History Of The Atom Ck 12 Foundation
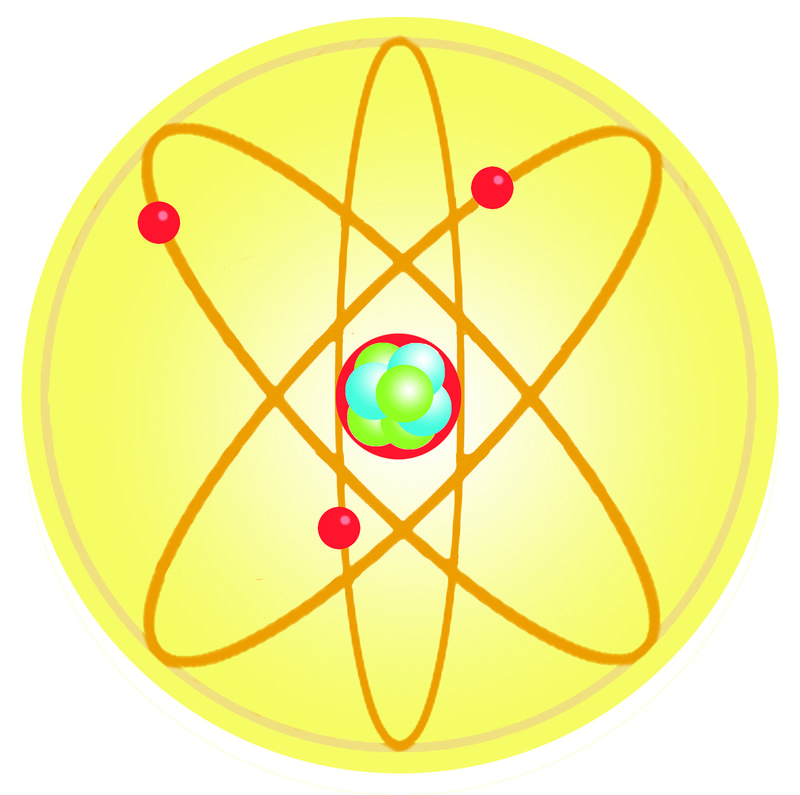
Dalton S Atomic Theory Read Chemistry Ck 12 Foundation
Subatomic Particles

The Structure Of The Atom Boundless Chemistry

Modeling Atoms Pratyusha S Science Notebook

8 5a Atomic Structure Flashcards Quizlet

Atom Definition History Examples Britannica

Introduction To Structure Of Atom Proton Neutron Electron With Examples
Sub Atomic Particles Chemistry Libretexts
1 14 1 17 Atomic Structure
2 3 The Nuclear Atom Chemistry Libretexts

Sub Atomic Particles Chemistry Libretexts
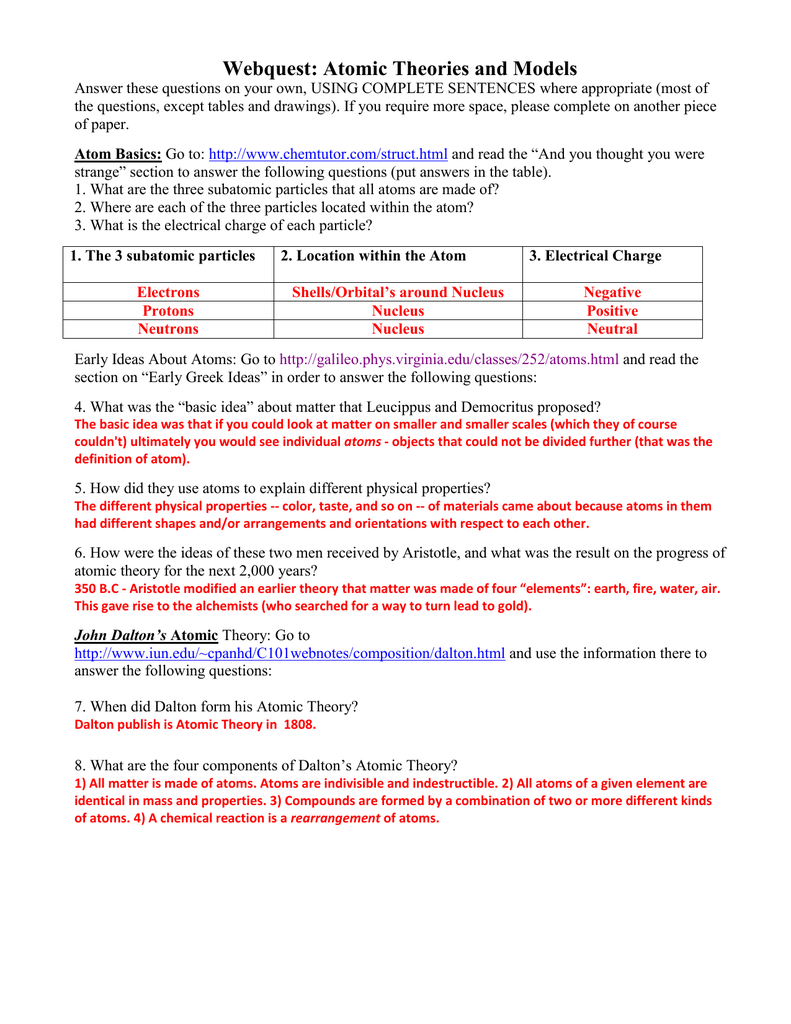
Webquest Atomic Theories And Models
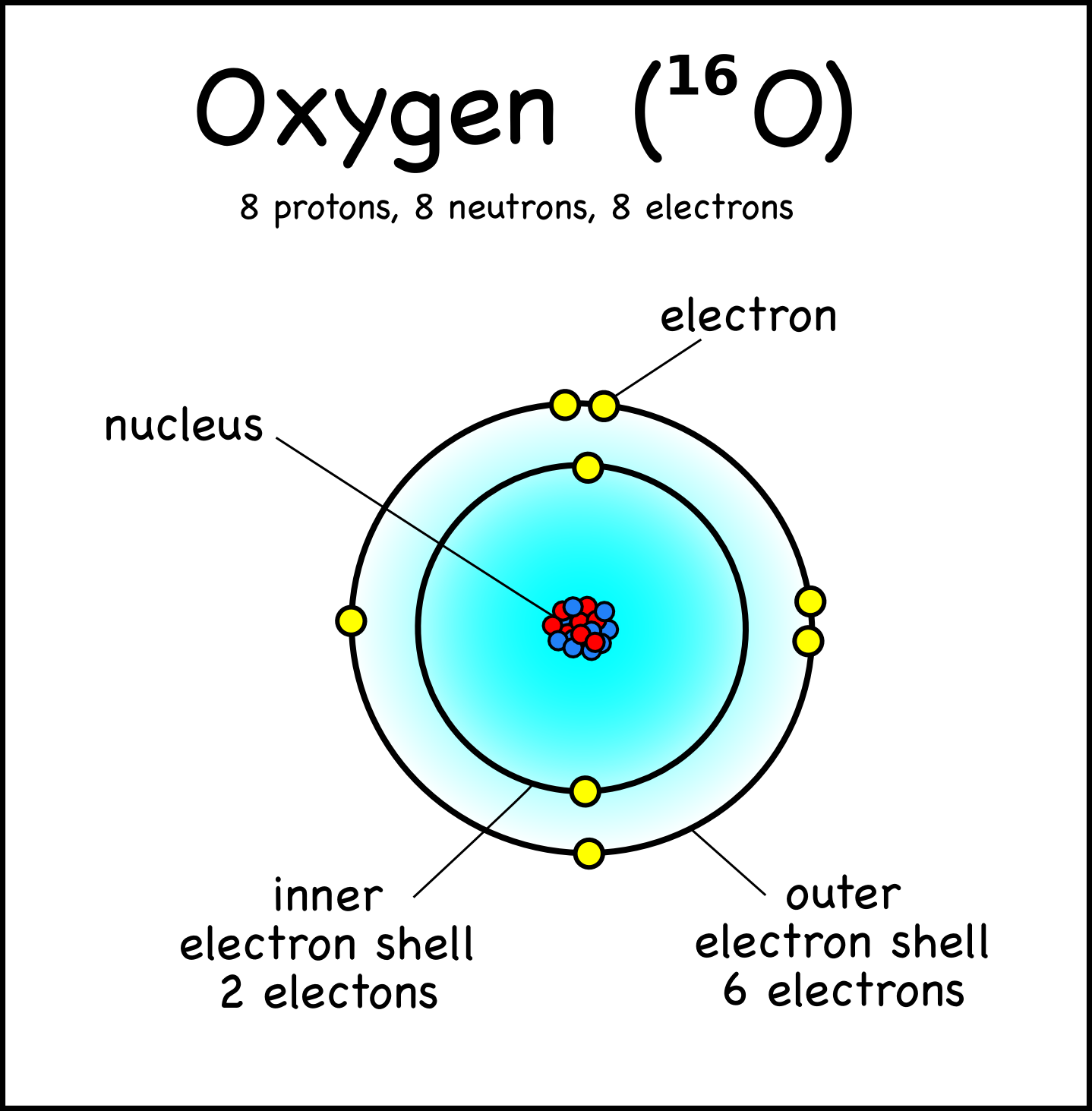
Drawing Atoms Montessori Muddle

Subatomic Particle Subatomic Particle Helium Atom Chemical Element Science Chemical Element Sphere Particle Png Pngwing

Chem4kids Com Atoms Structure
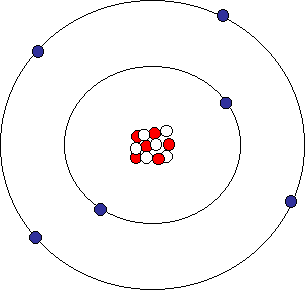
Atomic Structure

5 Atom Models Atom Models Bohr Chemistry En Nuclear Plum Pudding Science Solid Sphere Wave Mechanical Glogster Edu Interactive Multimedia Posters

Elementary Particles
Q Tbn 3aand9gctpcdvejjdp0km56cdlgim5w3ytaj1vwn8mlckl9azwjwemrmf Usqp Cau
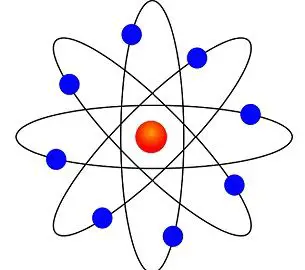
Difference Between Bohr And Rutherford S Atomic Models With Comparison Chart Bio Differences

The History Of The Atom Theories And Models Compound Interest

Ps 2 1 Compare The Subatomic Particles Protons Neutrons

Atoms Lesson Plan A Complete Science Lesson Using The 5e Method Of Instruction Kesler Science

Bohr Model Description Development Britannica

Chem4kids Com Atoms Structure
Atom Wikipedia
/GettyImages-141483984-56a133b65f9b58b7d0bcfdb1.jpg)
Basic Model Of The Atom Atomic Theory
What Are The Names Charges And Locations Of The Three Types Of Subatomic Particles That Make Up An Atom Socratic
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Bx0i9g23eukeznnxw1e8sio52gsmrvhbg4m22itzhgxh4hfv Usqp Cau
What Are The Components Of The Atomic Structure

2 1 Elements And Atoms The Building Blocks Of Matter Fvcc104 2 Chemistry Fvcc104 Openstax Cnx

The Early Atom Boundless Physics

Elementary Particles
Electron Wikipedia
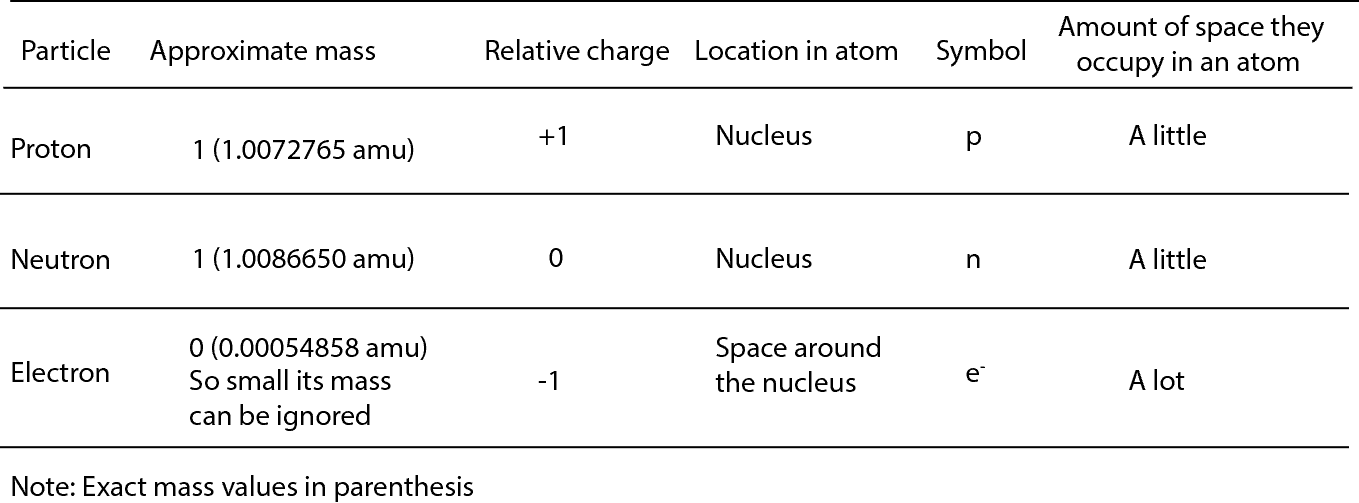
What Re The Properties Of The Subatomic Particles And How Are These Particles Related

5 Atom Models Atom Models Bohr Chemistry En Nuclear Plum Pudding Science Solid Sphere Wave Mechanical Glogster Edu Interactive Multimedia Posters

Chem4kids Com Atoms Structure
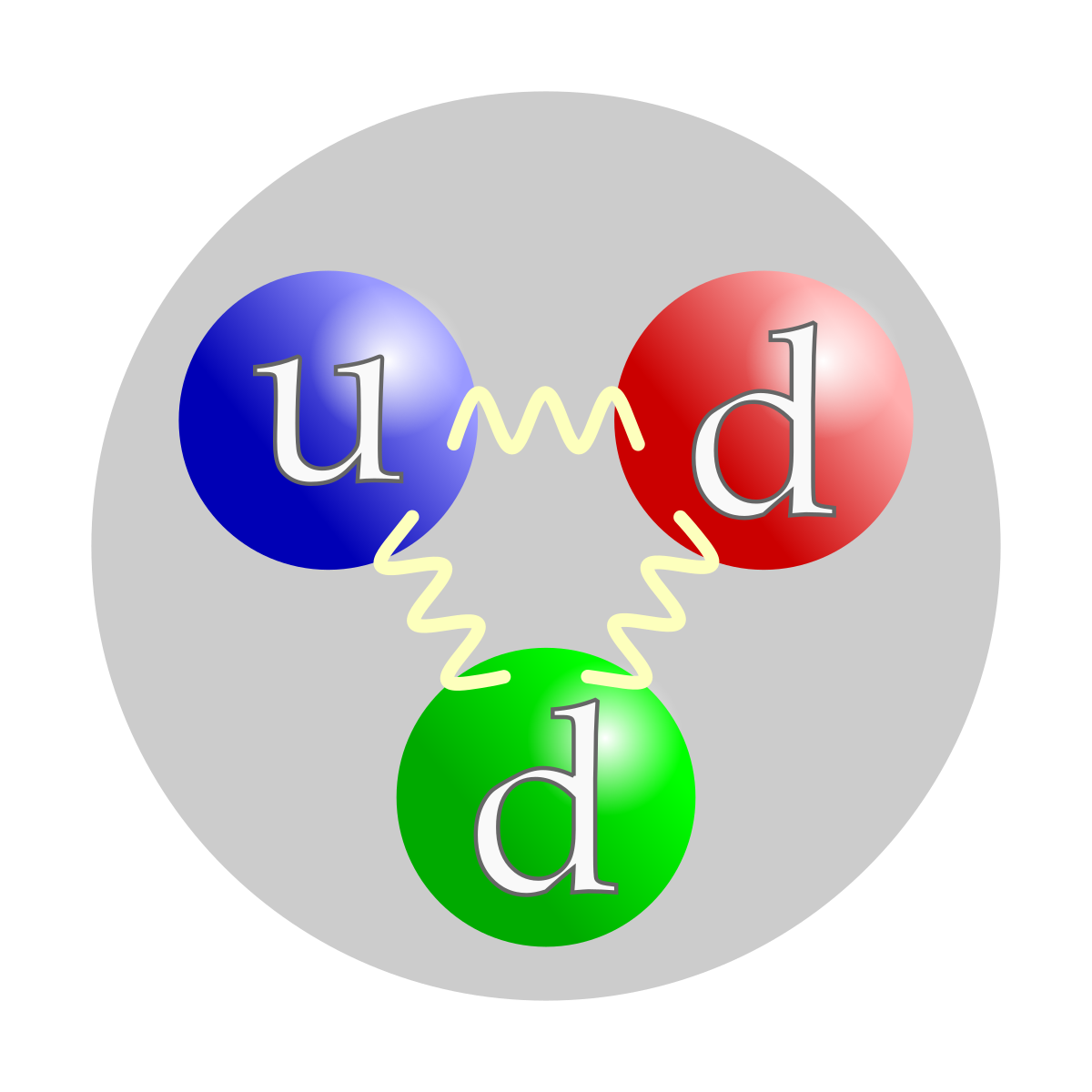
Neutron Wikipedia

Structure Of Atom Class 11 Chemistry India Science Khan Academy
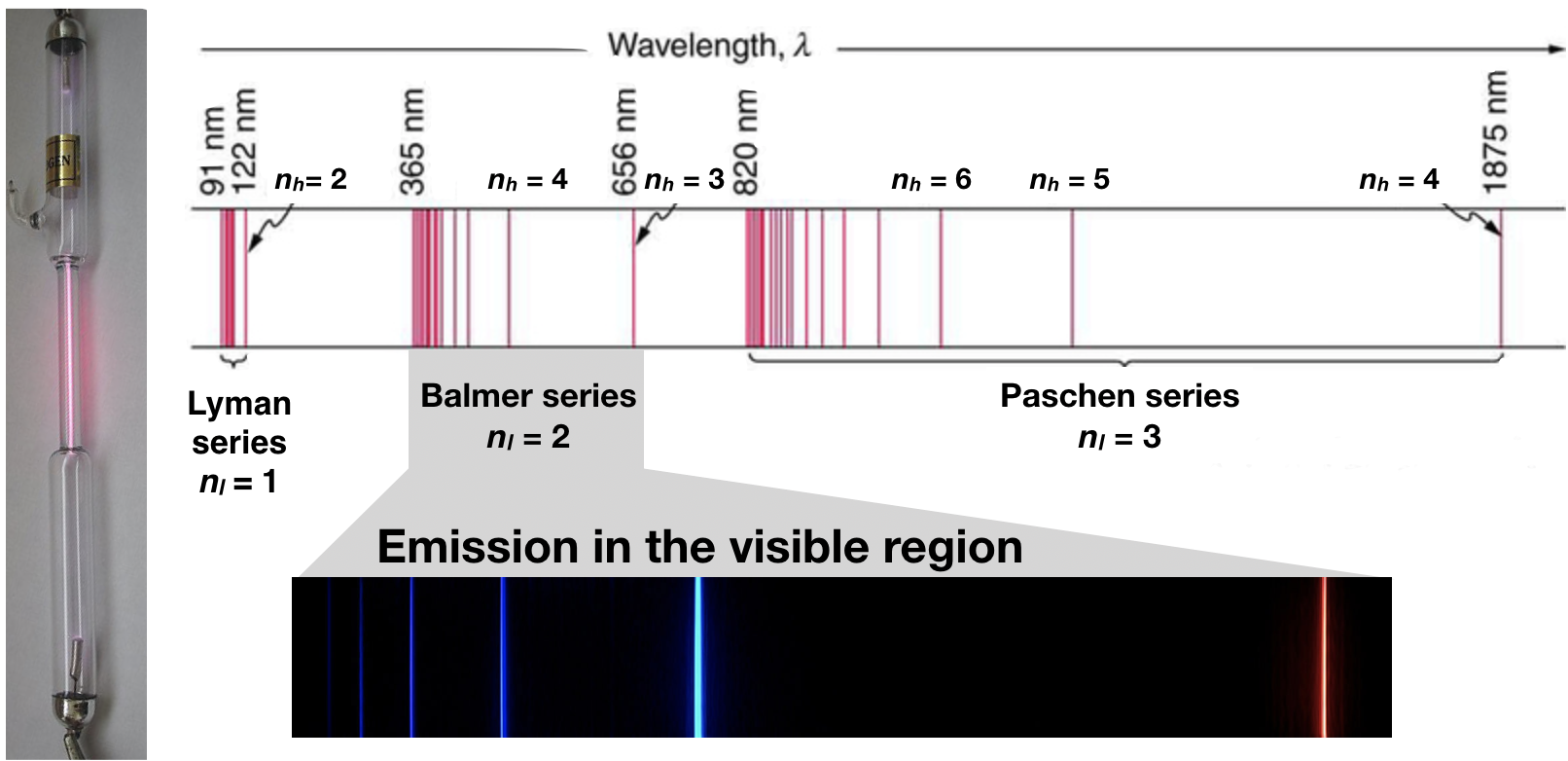
2 1 2 Discovery Of Subatomic Particles And The Bohr Atom Chemistry Libretexts
/atom-drawn-by-scientist-or-student-155287893-584ee6855f9b58a8cd2fc8f1.jpg)
Subatomic Particles You Should Know

Bohr Model Atomic Theory Subatomic Particle Science Electron Transparent Png

What Are The Parts Of An Atom

What Are The Parts Of An Atom Universe Today

Elementary Particles

Subatomic Particle Atomic Nucleus Atomic Physics Particles Miscellaneous Text Png Pngegg

What Is An Atom It S A Question Of Physics The Atomic Age Linda Hall Library Kansas City Mo

Untitled Document
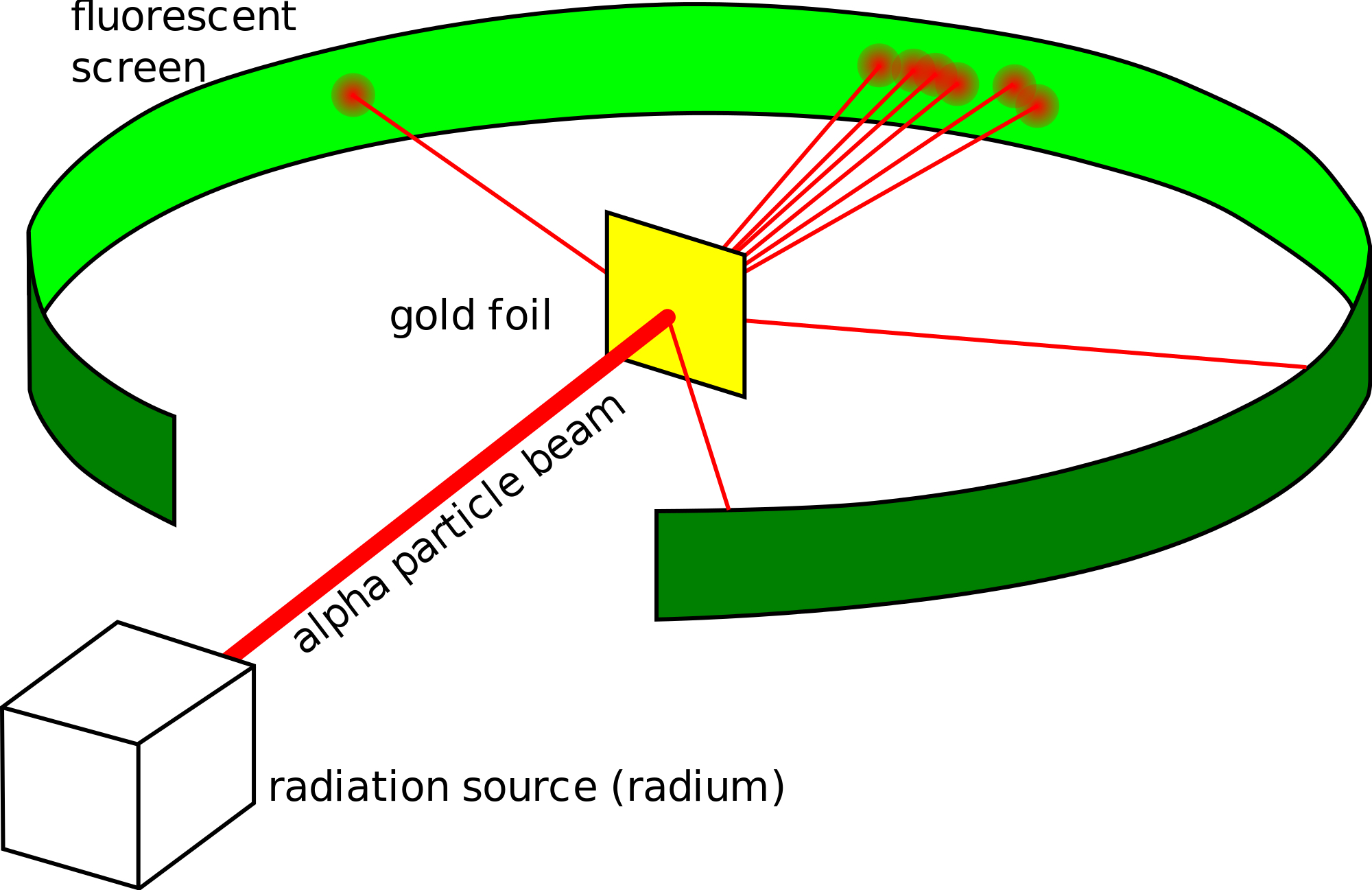
Experimental Evidence For The Structure Of The Atom
Subatomic Particle Wikipedia

Atomic Structure Electrons Protons Neutrons And Atomic Models



