Model Of A Neuron Vesicle
Also when we zoomed in on the first four bursts of 50 action potentials, the number of fusion events was significantly lower in CAPS DKO neurons compared to WT.

Model of a neuron vesicle. DeSantis1, Wei-Ping Li1, Erin K. (b) In this pseudo-colored image from a scanning electron microscope, a terminal button (green) has been opened to reveal the synaptic vesicles (orange and blue) inside. And if postsynaptic receptors were invariably saturated by the.
The kinetic model for vesicle release has two calcium sensors, a sensor for fast synchronous release that lasts a few tens of milliseconds and a separate sensor for slow asynchronous release that lasts a few hundred milliseconds. Nearly all plant cells and many protists and fungi have a central fluid-filled compartment called the vacuole.It contains ions, sugars, amino acids, some proteins, enzymes, and waste. Neuron-like means they share properties similar to neurons, in this case it is referring to releasing neurotransmitter by vesicles.
A presynaptic neuron makes M functional contacts onto a postsyn-aptic neuron. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Start studying Model of a Neuron.
Vesicles are found in bacteria, Archea, and plants as well as in animals.In each cell they have a distinct function and the same cell can have different types of vesicles, involved in various roles. With a discrete set of nerve-terminal vesicles. The last attractive model is a two-state model where a DS can accommodate one bound vesicle in two different states (loosely docked state and tightly docked state).
Therefore, the immunohistochemical pattern of the synaptic vesicle marker, synaptophysin, was examined to identify reductions in vesicle abundance and hence nerve terminals. Conceptual Model Capacitor Simulation Computational implementation of the conceptual model We're going to use the CellBuilder to make a cell that has surface area = 100 um2 and no ion channels. Although clathrin-coated vesicles (CCVs) are found ubiquitously in all eukaryotic cells and tissues, their components are particularly enriched in the brain (Galli and Haucke 04;.
We explore the properties of models of synaptic vesicle dynamics, in which synaptic depression is attributed to depletion of a pool of release-ready vesicles. Synaptic vesicle (white ball) "Axon Terminal model" A. (Association neuron cell body) C.
Synaptic vesicles are shown in Figure 16.14, which is an image from a scanning electron microscope. In this issue of Neuron, Nakamura et al. Lemire , View ORCID Profile Michael C.
In this model, receptors are capable of binding. Both methods indicated that for release. However, one missing link in the synaptic vesicle-VGCC coupling debate has been a description of VGCC topography at the release sites in presynaptic active zones (AZs).
In an exemplar 3D trajectory , a single vesicle in a living neuron underwent ~12 s of intense movement, travelling almost unidirectionally with the net displacement of 3.2 μm over 90 s of imaging, with dwelling in two discrete zones, presumptive presynaptic terminals marked by distinct clouds of vesicles labeled with FM 4-64, a lipophilic. Mitochondria "Axon Terminal model" C. This model was proposed based on the evidence that the docked/primed synaptic vesicle state is very dynamic ( Neher and Brose, 18 ;.
In their model, all but instead increased the number of vesicles available synaptic vesicles are divided into two pools, available. Figures 5C–5E, red symbols and lines). Start studying Neuron Model.
The release of membrane-bound vesicles is a universally conserved cellular process that occurs in all three domains of life (Deatherage and Cookson 12;. Upon widening of the pore the complex disassembles by the inclusion of mobile lipids, and full fusion occurs. Neurons have diverse vesicles with different sequence biogenesis and secretory steps.
Hines and Carnevale, 1997). It also suggests how age-dependent decline in α2- and β1-AR expression leads to decreased NA release in. Motor neuron (myelinated axon) #7.
The large dense core vesicles (LDCV) (from 75-95 nm) deliver proteins and neuropeptides to the extracellular space by the classic secretory pathway, while more numerous smaller vesicles (40-50 nm) called SV, specialize in the storage and delivery for small NTs such as monoamines, GABA, glycine, glutamate. Importantly, we show that motor neuron degeneration in these mutant dynactin mice is associated with abnormalities in intracellular vesicular trafficking, axonal swelling and axo-terminal. Until recently, a consensus formed that after exocytosis, SVs are recovered by either fusion pore closure (kiss-and-run) or clathrin-mediated endocytosis directly from the plasma membrane.
The last attractive model is a two-state model where a DS can accommodate one bound vesicle in two different states (loosely docked state and tightly docked state). Of unprimed (U) and primed (V) vesicles being fixed at average RRP sizes (Millar et al., 02, 05), only the initial total number Neuron Model of Transmitter Release and Plasticity Neuron 62, 539–554, May 28, 09 ª09 Elsevier Inc. It also attempts to explain how Golgi-specific enzymes are recycled.
This model proposes that COPI vesicles move in two directions:. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell.The area in the axon that holds groups of vesicles is an axon terminal or "terminal bouton". Protein-protein interactions mediate the formation of a supramolecular complex that operates as the reversible fusion pore.
Harald Sontheimer, in Diseases of the Nervous System, 15. This neuronal model differs from conductance-based Hodgkin-Huxley-type models (13). EVs carry protein, lipid, and genetic cargo, and research over more than a decade has shown that they contain the misfolded.
Tancredi , View ORCID Profile Andrew L. Anterograde vesicles carry secretory proteins, while retrograde vesicles recycle Golgi-specific trafficking proteins. In the wild type, following uncoating, vesicles may either directly re-enter the vesicle pool or fuse with early endosomes for protein sorting and vesicle budding into new synaptic vesicles, thereby.
Synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A) is an abundant membrane-bound glycoprotein that is found on secretory vesicles including synaptic vesicles. Plus more code. The dynamics of vesicles accumulating in MPSIIIB neuron processes therefore differed from normal lysosomes.
PC12 cells stop dividing and terminally differentiate when treated with nerve growth factor or dexamethasone. Posterior root ganglion (Sensory neuron cell body) D. This was consistent with a model in which synaptic vesicles at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses underwent full fusion.
Neurotransmitter (brown in white ball) "Axon Terminal model" B. Rough pink outer layer. However, recent data have revealed that SV formation is more complex than previously.
(15), is the clustered VGCC-random vesicle placement model (random placement model;. (Hasenstaub et al., 10;. Meinrenken et al., 02).
1).The production of these extracellular vesicles (EVs) has been systematically observed each time researchers have investigated this phenomenon, suggesting that all cells are potentially capable of. This makes PC12 cells useful as a model system for neuronal differentiation and neurosecretion. After releasing a docked vesicle, a contact enters a refractory period in which it is.
Physical System An electrolyte-containing vesicle with a lipid bilayer membrane that has no ion channels. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse.The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel.
Synaptic Vesicle Protein 2A. Neurotransmission is sustained by endocytosis and refilling of synaptic vesicles (SVs) locally within the presynapse. Smith and Betz, 1996).
It is possible that each synapse type employs a particular mode of endocytosis. SNARE proteins – "SNAP REceptor" – are a large protein family consisting of at least 24 members in yeasts and more than 60 members in mammalian cells. These vesicles were larger in MPSIIIB (0.71 ± 0.03 μm 2, n = 295) than in wild type (0.54 ± 0.02 μm 2, n = 185, P < 0.01) neurons, and more frequently immobile (72.2% versus 49.7%).
The model explains observations of compartments, polarized distribution of enzymes, and waves of moving vesicles. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) include exosomes and microvesicles and have been shown to have roles in the CNS ranging from the removal of unwanted biomolecules to intercellular communication to the spread of pathogenic proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. This notably mediates exocytosis, but can also mediate the fusion of vesicles with membrane-bound compartments (such as a.
A dense network of synaptophysin IR was found in all parts of the spinal cord grey matter of 70-day-old control ( Fig. The quantal nature of neurotransmitter release is often considered to provide the elemental unit for information processing by the nervous system. Each vesicle contains about 10,000 neurotransmitter molecules.
In this model, VGCCs are placed in clusters, while vesicles are placed randomly throughout the AZ, which results in a variable coupling. When slices were frozen s after HFS 100APs, the number of docked vesicles was 1.45 ± 0.04 per 100-nm active zone profile length (193 profiles, 4 mice;. When a presynaptic spike arrives, each docked vesicle is released with probability p r.
This model of random selection of weights comprising. We propose a model in which p-NAP me- diates vesicle transport between the soma and the axon terminus and suggest that J~-NAP may represent. Alternatively, multiple modes of endocytosis operate at the same synapse, and the synapse toggles between different modes depending on its activity level.
Model that also includes a clustered VGCC topography, as was observed by Nakamura et al. (a) The synapse is the space between the terminal button of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. Our approach involves recording excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) from autapses on an isolated cultured hippocampal pyramidal neuron after applying bafilomycin A1 (Baf) to prevent refilling of empty vesicles with glutamate ().Baf is a cell-permeant blocker of the V-type ATPase, a proton pump that is required for SV reacidification after endocytosis (, 16).
Schatz and Vardi 18) (Fig. Driven transport and delivery of vesicles to synaptic targets along the axon of a neuron. When nucleofected, striatal and habenula neurons were.
Murthy and De Camilli 03).Clathrin, the heterotetrameric adaptor complex (AP-2), as well as monomeric adaptors and accessory proteins including epsin, epsl5, AP180, HIP1/HIP1R, and amphiphysin, play an early role. Currently, it is not clear whether a universal model of vesicle recycling exist for all types of synapses. The simulations used an integration step size of 0.1 ms, but were checked with a reduced step of 0.01 ms.
Smooth outer pink (#5) endomysium. In this model, the stabilization of adaptors on the vesicle in the absence of UNC-26, also results in the retention of the clathrin coat. We used Liu and Tsien’s simplified model serotonin had little effect on the rate of vesicle cycling, (1995) to analyze this depression.
It is an essential protein;. Alternatively, we could do this in HOC create soma. Axon terminals (also called synaptic boutons, terminal boutons, or end-feet) are distal terminations of the telodendria (branches) of an axon.An axon, also called a nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses called action potentials away from the neuron's cell body, or soma, in order to transmit those impulses to other neurons.
The kiss-and-run model Diagrammatic representation of three possible pathways for vesicle fusion after the vesicle has docked with to the presynaptic membrane;. Supplementary Figure 5 proposes a model to explain the relationship between sympathetic and motor neurons and the role of ARs in regulating Ca 2+ channels, intracellular Ca 2+ concentration, and AChR synaptic vesicle release at the NMJ. This model was proposed based on the evidence that the docked/primed synaptic vesicle state is very dynamic ( Neher and Brose, 18 ;.
Mice with homozygote deletion die within 3 weeks after birth. Two alternative formulations of the model allow for either recruitment of vesicles from an unlimited reserve pool (vesicle state model) or for recovery of a fixed number of release sites. The LRRK2 G19S mutation alters astrocyte-to-neuron communication via extracellular vesicles and induces neuron atrophy in a human iPSC-derived model of Parkinson’s disease Aurelie de Rus Jacquet1*, Jenna L.
7 A) and SOD1 mice ( Fig. The average vesicle fusion rate during stimulation, calculated from the cumulative release plots , was 1.2±0.4 vesicles/s for WT compared to 0.15±0.1 vesicles/s for CAPS DKO neurons. The LRRK2 G19S mutation alters astrocyte-to-neuron communication via extracellular vesicles and induces neuron atrophy in a human iPSC-derived model of Parkinson’s disease View ORCID Profile Aurelie de Rus Jacquet , Jenna L.
These results establish I~-NAP as a neuron-specific vesicle coat protein. SV2A has been identified as the binding site for the AED levetiracetam. There was more expression of miR-184, miR-137, miR-124 and miR-132 in neurons.
7 C, and Table 1 ). The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate vesicle fusion – the fusion of vesicles with the target membrane;. Changes in synaptic strength are generally thought to involve the probability of exocytotic release and the postsynaptic response, rather than the amount of neurotransmitter per vesicle.
DeSantis , Wei-Ping Li , View ORCID. N max in this model governs the strength of depression immediately after vesicle release (strongest depression for N max = 1) and represents an “effective” number of vesicles that takes into account both the possibility of having a population of vesicles with heterogeneous probabilities of release and the postrelease refractoriness thought. (c) miRNAs studied in the ADSC induced into neuron-like cells by co-culture or by extracellular vesicles on day 3.
Here, we document that a novel mouse model expressing human mutant p150 Glued dynactin exhibits clinical and pathological hallmarks of motor neuron disease. Epidural Space "Transverse section of spinal cord" A. Experimental evidence suggests that the distribution of vesicles along the axon is relatively uniform and that vesicular delivery to synapses is reversible.
The model neuron used the Hodgkin and Huxley formalism. The firing threshold in the model (as in real neurons) is not a parameter but a dynamic property that depends on the state of the neuron. (15) propose a new model for calcium sensor VGCC coupling using quantitative ultrastructural imaging to constrain VGCC topography.
A recent modeling study has made explicit the crucial role that. Models were build using the NEURON® simulation package (V7.1, Linux version;. This pseudocolored image taken with a scanning electron microscope shows an axon terminal that was broken open to reveal synaptic vesicles (blue and orange) inside the neuron.
Each functional contact can dock at most one neu-rotransmitter vesicle at a time. We study local calcium dynamics leading to a vesicle fusion in a stochastic, and spatially explicit, biophysical model of the CA3-CA1 presynaptic bouton. Instead of reproducing all of the ionic currents, the model was designed to reproduce firing responses;.
Learning Objectives And More Terms From Ccf Physiology L9 Synaptic Transmission Flashcards Memorang

Neuronal Bin1 Regulates Presynaptic Neurotransmitter Release And Memory Consolidation Sciencedirect

Exosomes And Other Extracellular Vesicles In Neural Cells And Neurodegenerative Diseases Sciencedirect
Model Of A Neuron Vesicle のギャラリー
Frontiers Revisiting The Role Of Clathrin Mediated Endoytosis In Synaptic Vesicle Recycling Cellular Neuroscience

Synaptic Vesicle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Extracellular Membrane Vesicles Mediated Mechanisms In Neurons A A Download Scientific Diagram

A Discrete Presynaptic Vesicle Cycle For Neuromodulator Receptors Neuron December 19

A Presynaptic Model For Working Memory Deficits Calcineurin Deficiency Download Scientific Diagram

Jci Extracellular Vesicles And Intercellular Communication Within The Nervous System

Atm And Atr Play Complementary Roles In The Behavior Of Excitatory And Inhibitory Vesicle Populations Pnas

Presynaptic Terminal An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
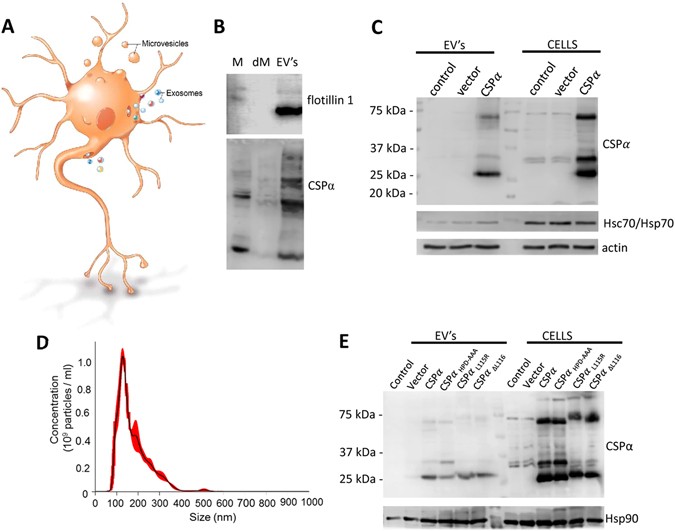
Neurons Export Extracellular Vesicles Enriched In Cysteine String Protein And Misfolded Protein Cargo Scientific Reports
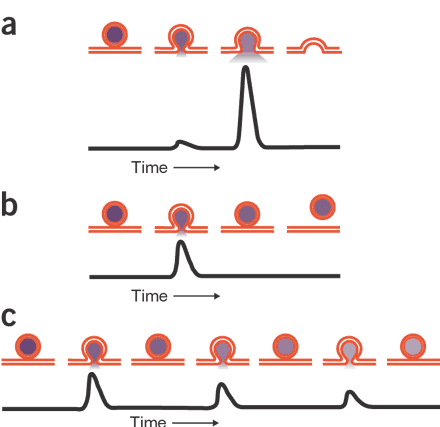
Synaptic Vesicles Really Do Kiss And Run Nature Neuroscience

Endosomal Sorting Of Readily Releasable Synaptic Vesicles Pnas
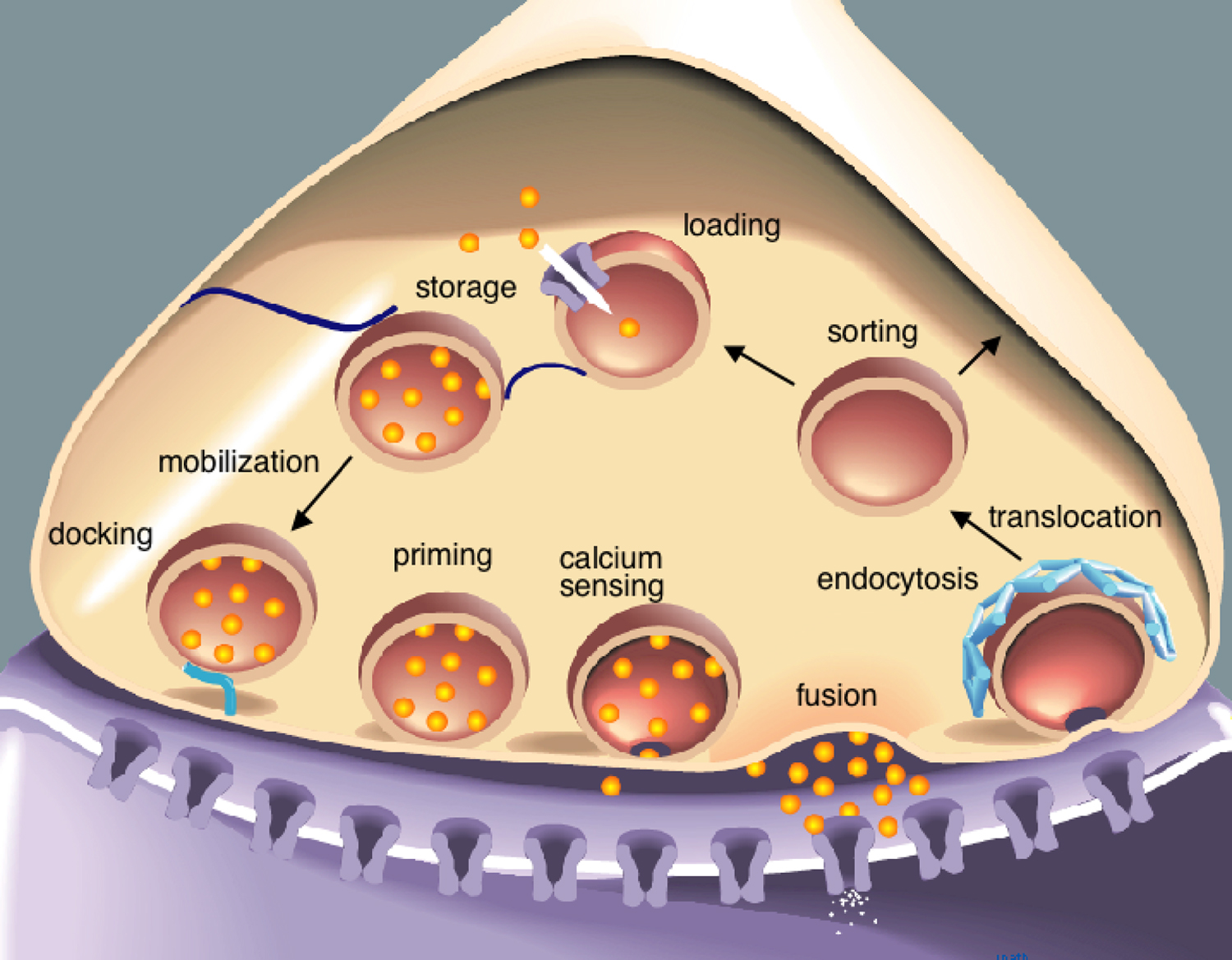
Molecular Regulation Of Synaptic Release Springerlink
Plos Genetics Bioenergetic Status Modulates Motor Neuron Vulnerability And Pathogenesis In A Zebrafish Model Of Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Synapse Wikipedia

Synaptic Vesicle Fusion Is Modulated Through Feedback Inhibition By Dopamine Auto Receptors Formisano Synapse Wiley Online Library

Synaptic Vesicle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
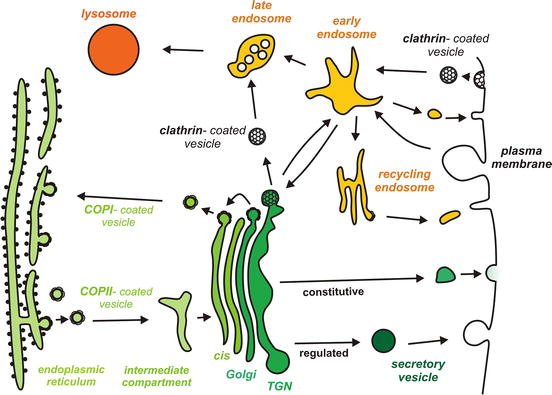
Frontiers Synaptic Vesicle Endocytosis In Different Model Systems Cellular Neuroscience

Extracellular Vesicles As Modulators Of Cell To Cell Communication In The Healthy And Diseased Brain Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society B Biological Sciences

Ctbp1 Mediated Membrane Fission Contributes To Effective Recycling Of Synaptic Vesicles Sciencedirect
Amyloid Precursor Protein Is Trafficked And Secreted Via Synaptic Vesicles

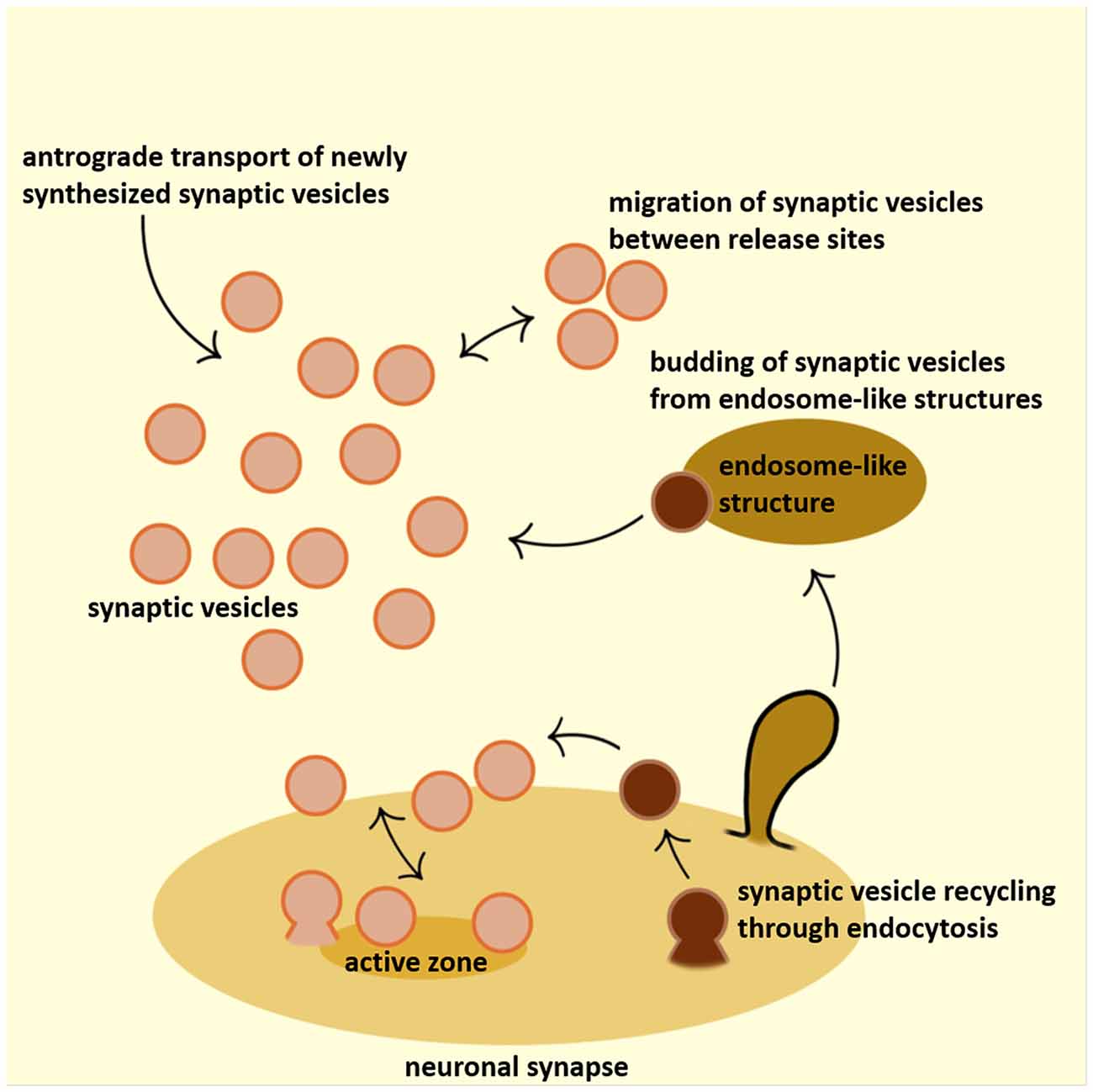
Synaptic Vesicle Precursors Rapidly Coalesce Into Puncta Behind The Download Scientific Diagram

Distinct Nanoscale Calcium Channel And Synaptic Vesicle Topographies Contribute To The Diversity Of Synaptic Function Neuron X Mol
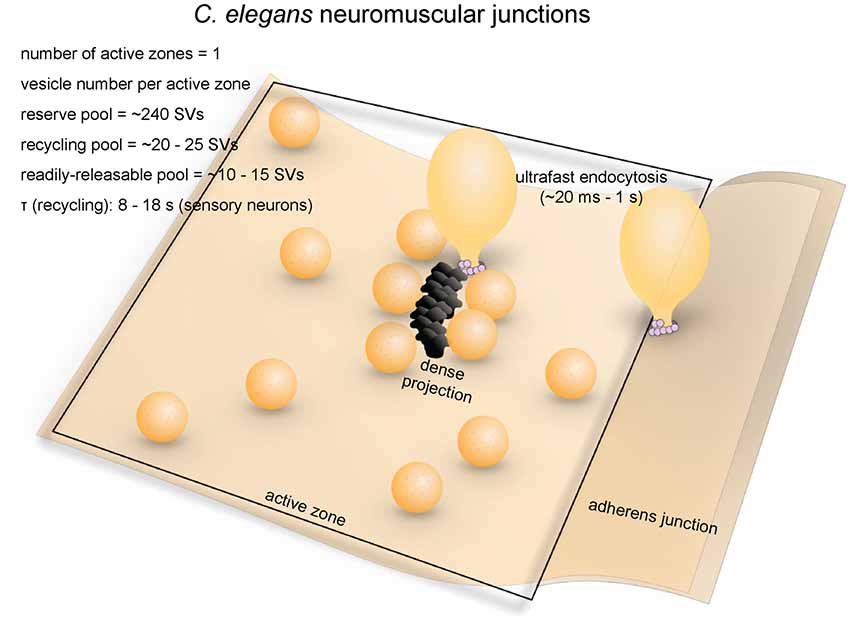
Synaptic Loss In Schizophrenia A Meta Analysis And Systematic Review Of Synaptic Protein And Mrna Measures Molecular Psychiatry

Neurotransmitter Release Mechanisms Neurotransmitters Are Packaged Into Synaptic Vesicles Transmit Signals F In Pretty Little Girls Pattern Drawing Photo Editing
Ultrastructural Examination Of Dispersal Of Synaptic Vesicles In Download Scientific Diagram

Gene Linked To Alzheimer S Disease Is Involved In Neuronal Communication Neuroscience News
Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1111 Epi 134
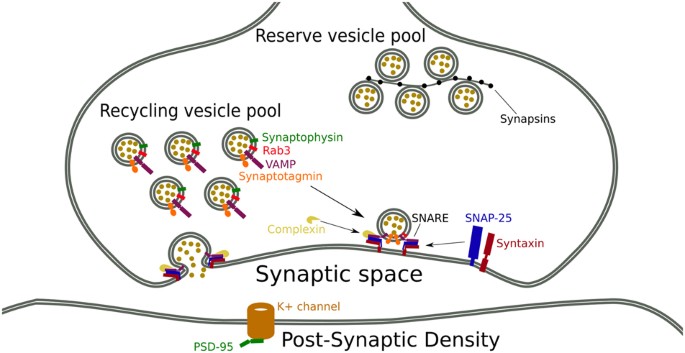
Synaptic Function

Synaptic Dysfunction Induced By Glycine Alanine Dipeptides In C9orf72 Als Ftd Is Rescued By Sv2 Replenishment Embo Molecular Medicine
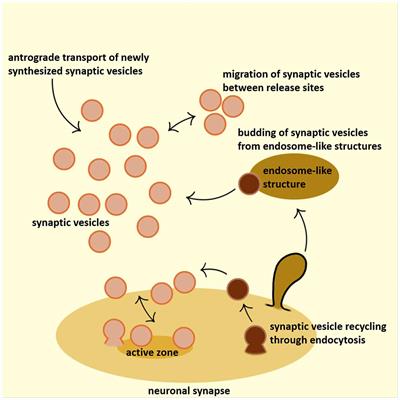
Frontiers Revisiting The Role Of Clathrin Mediated Endoytosis In Synaptic Vesicle Recycling Cellular Neuroscience

Extracellular Vesicles Multimodal Envoys In Neural Maintenance And Repair Trends In Neurosciences

Neurotransmitters And Receptors Article Khan Academy

Synaptic Vesicle Precursors And Lysosomes Are Transported By Different Mechanisms In The Axon Of Mammalian Neurons Sciencedirect

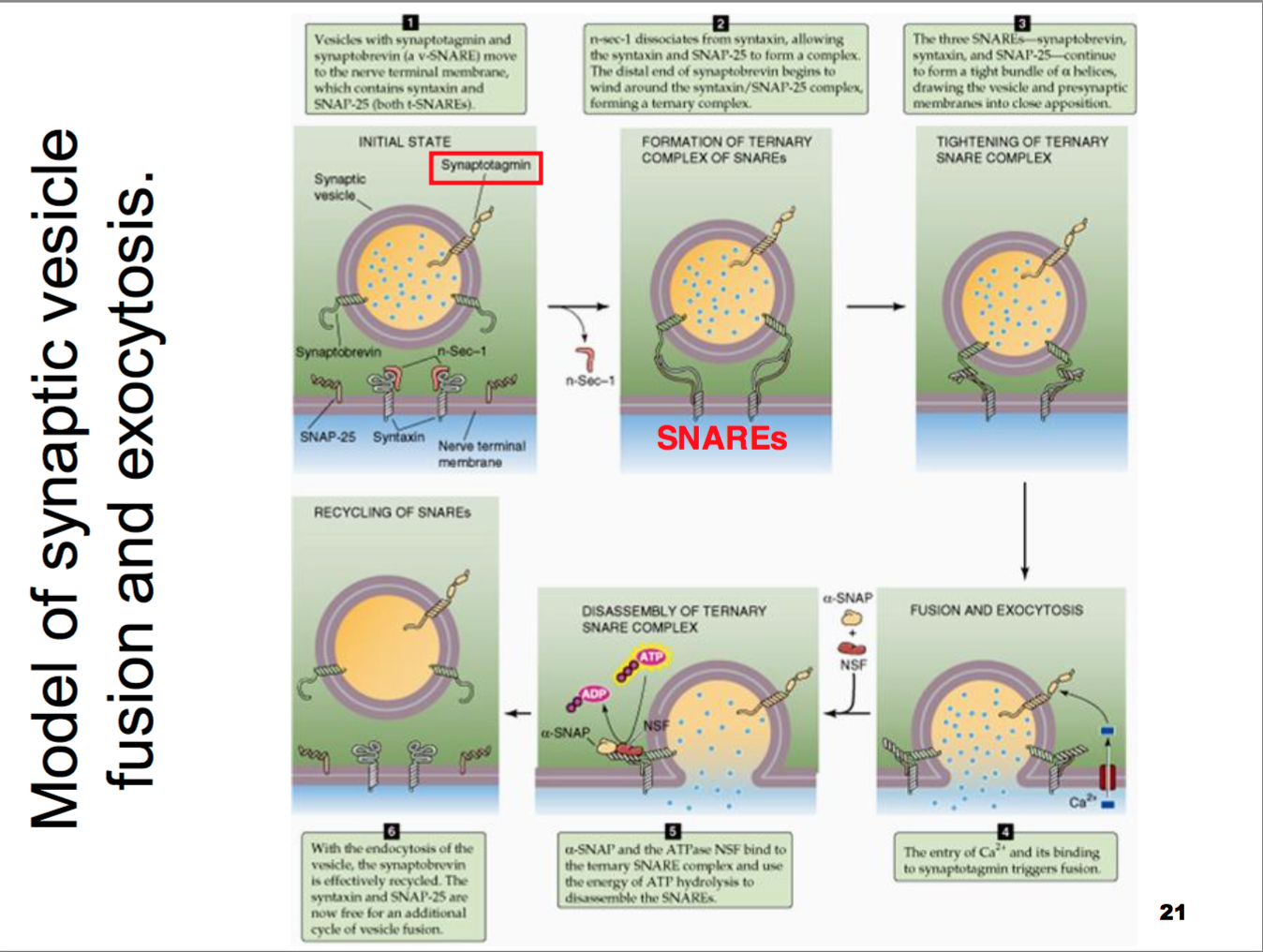
A Model Of The Role Of Snares In Mediating Membrane Fusion In Neuronal Download Scientific Diagram

How Does A Neuron Decide Which Synapses Will Release Neurotransmitter When A Neuron Spike Occurs Quora

Synaptic Dysfunction In Alzheimer S Disease The Effects Of Amyloid Beta On Synaptic Vesicle Dynamics As A Novel Target For Therapeutic Intervention Marsh J Alifragis P Neural Regen Res
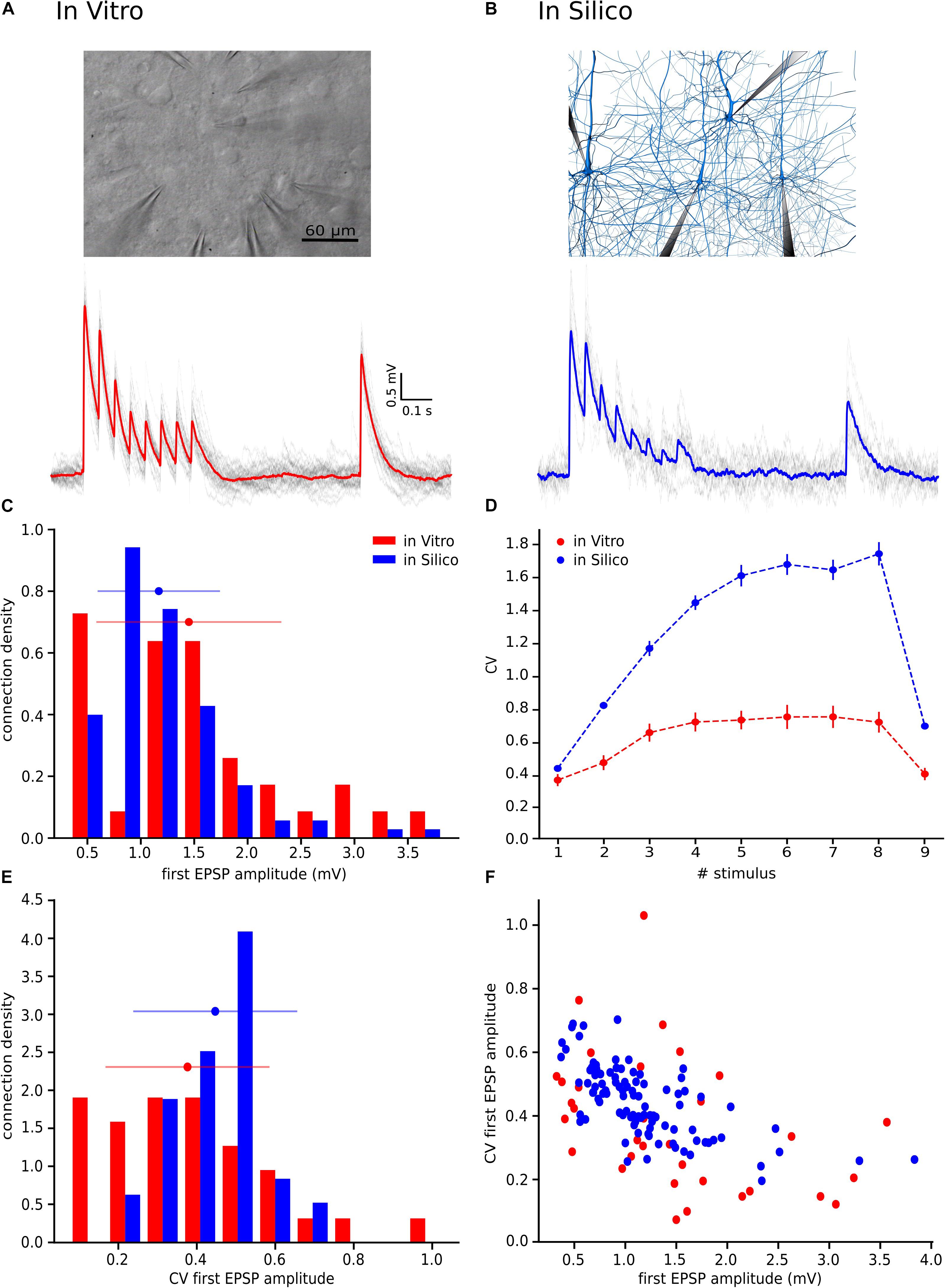
Frontiers Estimating The Readily Releasable Vesicle Pool Size At Synaptic Connections In The Neocortex Frontiers In Synaptic Neuroscience

Synaptic Vesicle Dynamics A The Axon Of A Presynaptic Neuron Download Scientific Diagram
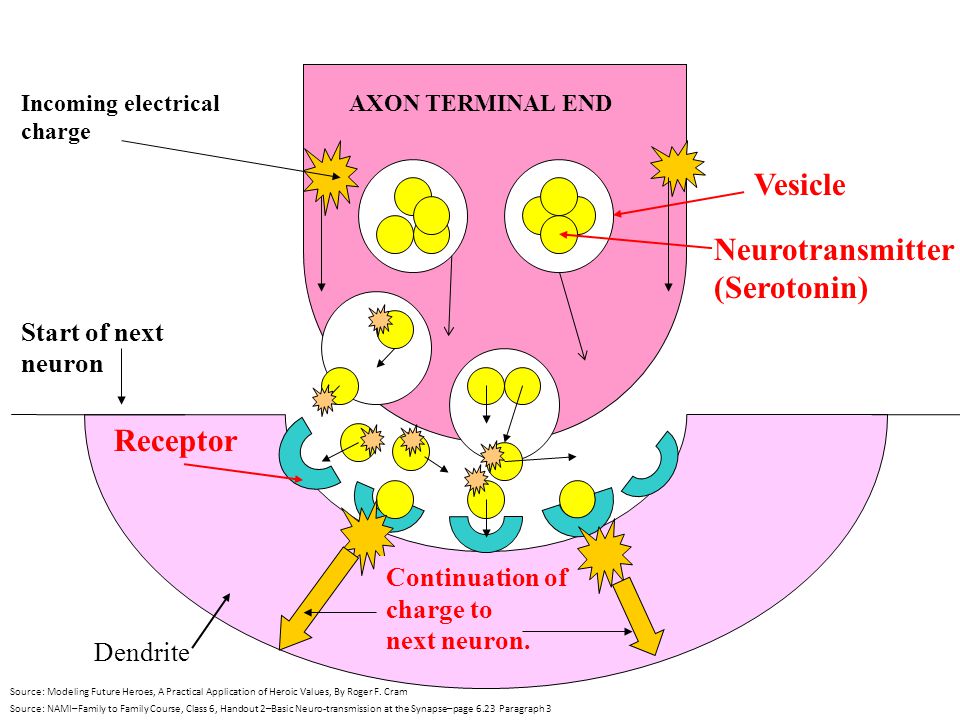
What Are Neurons What Are Neurotransmitters Ppt Download

The Reserve Pool Of Synaptic Vesicles Acts As A Buffer For Proteins Involved In Synaptic Vesicle Recycling Pnas

Chemical And Immunological Synapses Traffic

Visualizing Synaptic Vesicle Turnover And Pool Refilling Driven By Calcium Nanodomains At Presynaptic Active Zones Of Ribbon Synapses Pnas

Synaptic Vesicle Recycling An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Endosomal Sorting Of Readily Releasable Synaptic Vesicles Pnas

How Are Neurotransmitters Released From Vesicles In The Presynaptic Neuron Brain Stuff

Huntingtin Associated Protein 1 Is A Synapsin I Binding Protein Regulating Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis And Synapsin I Trafficking Mackenzie 16 Journal Of Neurochemistry Wiley Online Library

Variable Priming Of A Docked Synaptic Vesicle Pnas
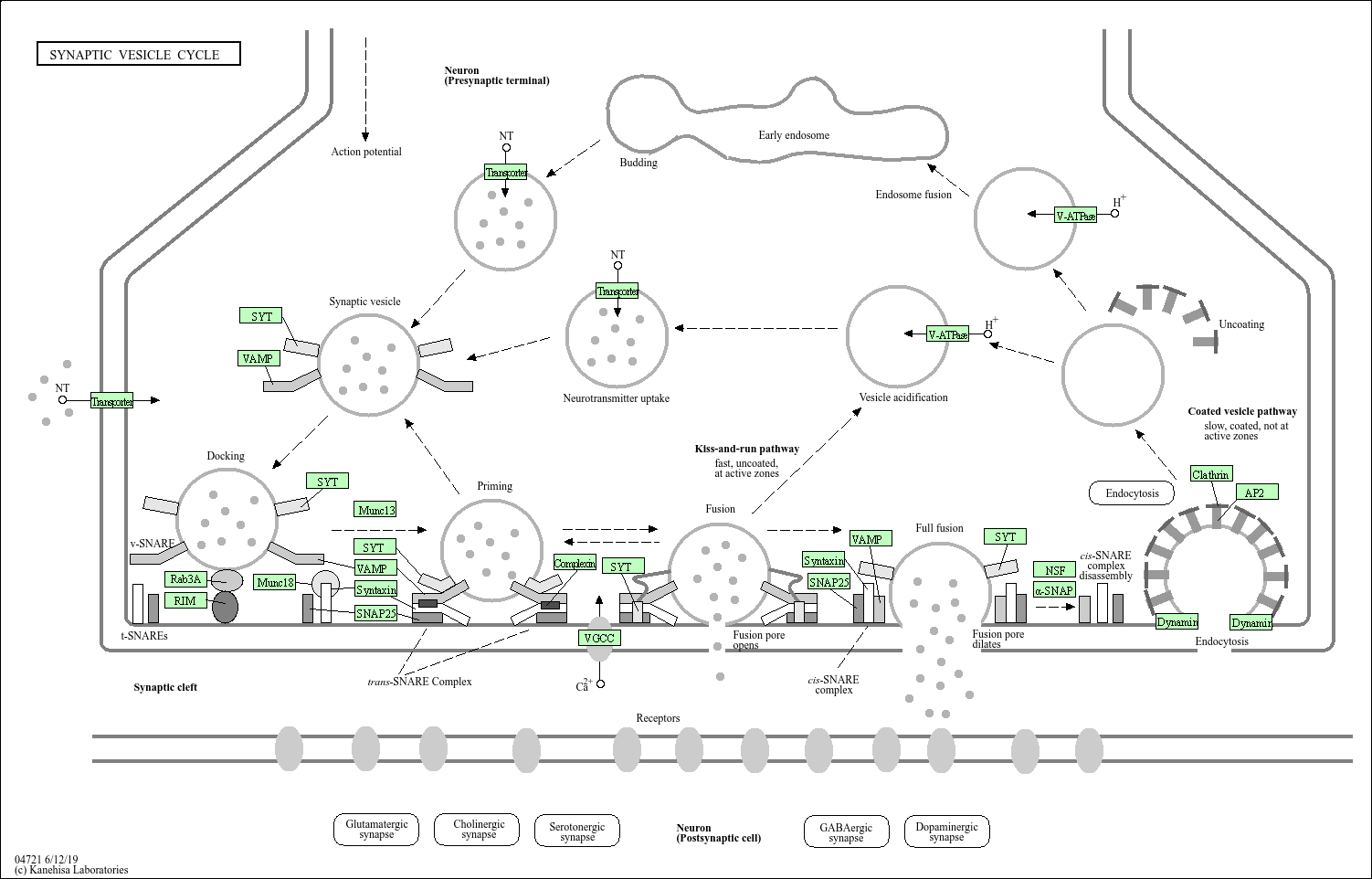
Kegg Pathway Synaptic Vesicle Cycle Homo Sapiens Human

Pre And Postsynaptic Mechanism In Neurons Activity On The Presynaptic Download Scientific Diagram
Neurotransmission Wikipedia

Model Of A Glutamatergic Synapse And The Molecular Circadian Clockwork Download Scientific Diagram

Synaptic Vesicle Recycling The Ferrari Of Endocytosis Sciencedirect

The Synaptic Vesicle Cycle Revisited New Insights Into The Modes And Mechanisms Journal Of Neuroscience

Electrophysiology And Modeling Of The Primary Auditory Neuron A The Download Scientific Diagram

Introduction To Neurons And Neuronal Networks Section 1 Intro Chapter Neuroscience Online An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences Department Of Neurobiology And Anatomy The University Of Texas Medical School At Houston

Neurotransmitter Release Biochemistry Britannica

Tj In A Neuron Synaptic Vesicles Or Neurotransmitter Vesicles Store Various Neurotransmitters That Are Released At Th Neurons Glial Cells Neurotransmitters
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqehq2kadgn0hrjvibnbtbug Qqhpauqlwepgii1sxngfzfr6zl Usqp Cau

Three Models For Where Neuronal Membrane Proteins Sort And Degrade A Download Scientific Diagram
Q Tbn 3aand9gctd8a54l7y105q0alqb7pmnk 4buv 61el Rdgaem2fdogusbvt Usqp Cau

Synaptic Vesicle Recycling Machinery Components As Potential Therapeutic Targets Pharmacological Reviews

Presynaptic Neurons Fine Tune Dopamine Signaling The Scientist Magazine
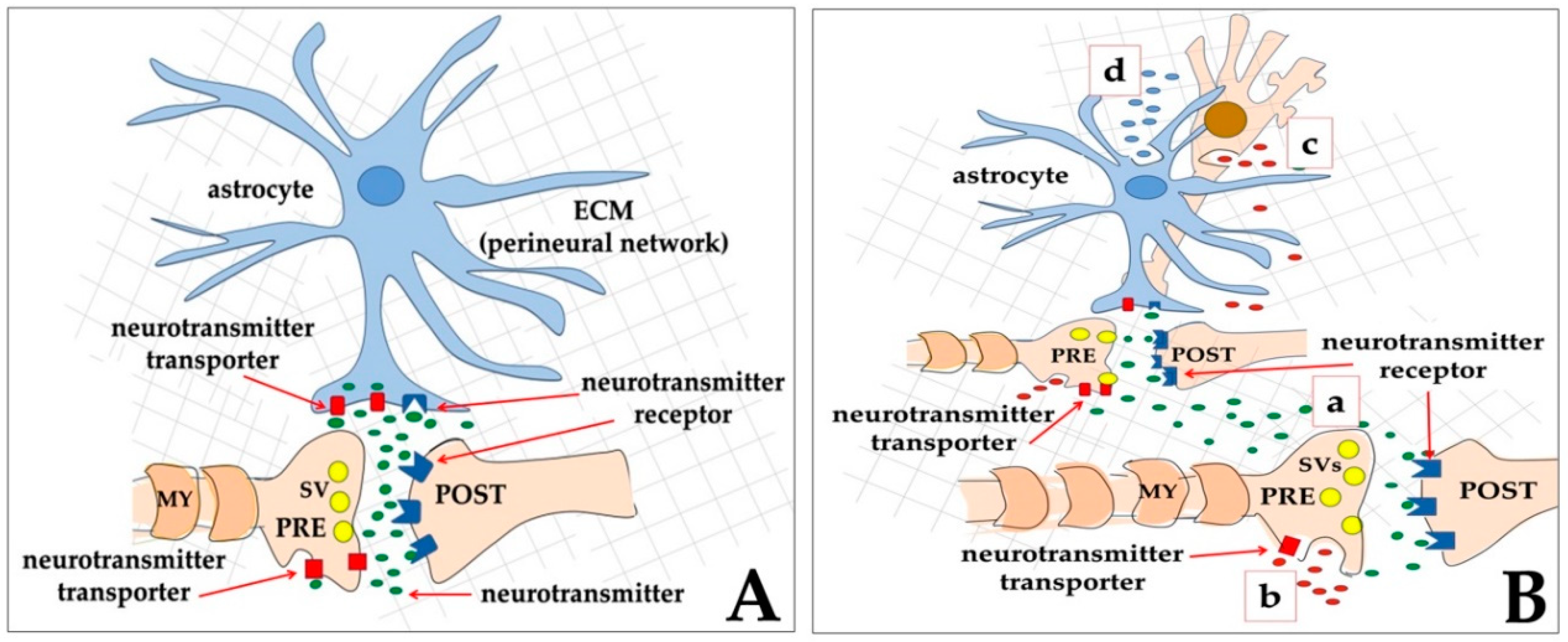
Ijms Free Full Text Cell To Cell Communication In Learning And Memory From Neuro And Glio Transmission To Information Exchange Mediated By Extracellular Vesicles Html

Exosomes And Other Extracellular Vesicles In Neural Cells And Neurodegenerative Diseases Sciencedirect

Figure 3 From Coupling Actin And Membrane Dynamics During Calcium Regulated Exocytosis A Role For Rho And Arf Gtpases Semantic Scholar

Loss Of Huntingtin Function Slows Synaptic Vesicle Endocytosis In Striatal Neurons From The Httq140 Q140 Mouse Model Of Huntington S Disease Sciencedirect
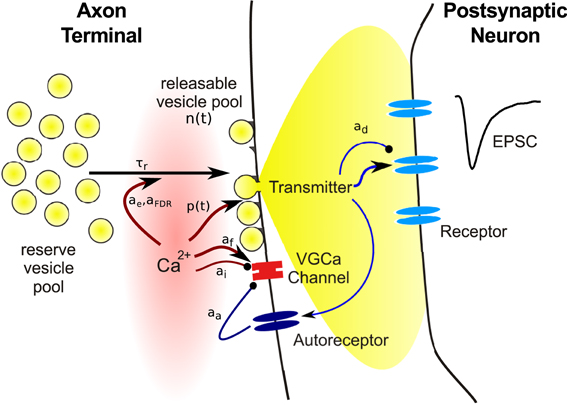
Frontiers Theoretical Models Of Synaptic Short Term Plasticity Frontiers In Computational Neuroscience

How Neurons Talk To Each Other Max Planck Gesellschaft

Elevated Synaptic Vesicle Release Probability In Synaptophysin Gyrin Family Quadruple Knockouts Elife

Synapse And Active Zone Assembly In The Absence Of Presynaptic Ca2 Channels And Ca2 Entry Neuron X Mol
Http Www Math Nyu Edu Faculty Peskin Papers Zhang Peskin 18 Preprint Pdf
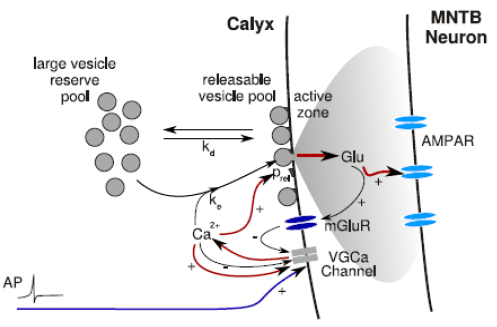
Synaptic Transmission

Phytic Acid Attenuates Upregulation Of Gsk 3b And Disturbance Of Synaptic Vesicle Recycling In Mptp Induced Parkinson S Disease Models Neurochem Int X Mol

Fig 3 Composition Of Isolated Synaptic Boutons Reveals The Amounts Of Vesicle Trafficking Proteins Science

Synaptic Vesicle Wikipedia

Axonal Transport Driving Synaptic Function Science

Actin Myosin V And Activity Dependent Inter Synaptic Vesicle Exchange In Central Neurons Sciencedirect
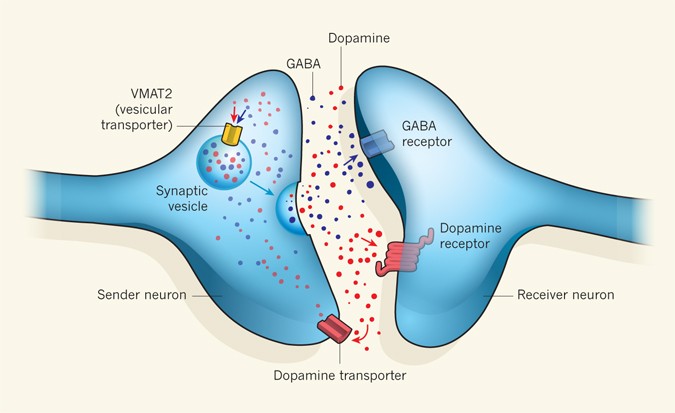
Promiscuous Vesicles Nature

Variable Priming Of A Docked Synaptic Vesicle Pnas

Partial Release Of Molecules From Living Neurons Chemviews Magazine Chemistryviews

Active Zone Wikipedia

Active Zone Wikipedia

Figure 4 From Cellular And Molecular Mechanisms Of Presynaptic Assembly Semantic Scholar

Proposed Model Of Polyamine Mediated Chemical Transmission In The Download Scientific Diagram
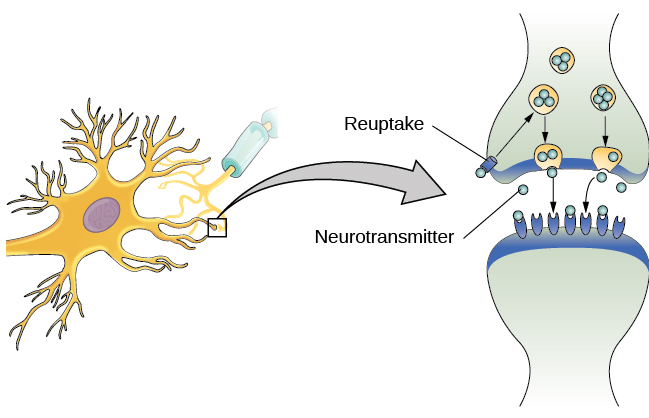
Neural Communication Introduction To Psychology
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsryniumyjtauzk5s1manl50h9 G10dn3mgpl99hug 8pgw5jc Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gct6x Honbf2mkc99z7ryds7eukq1xdxwtmorzt3gqn6nczag95p Usqp Cau
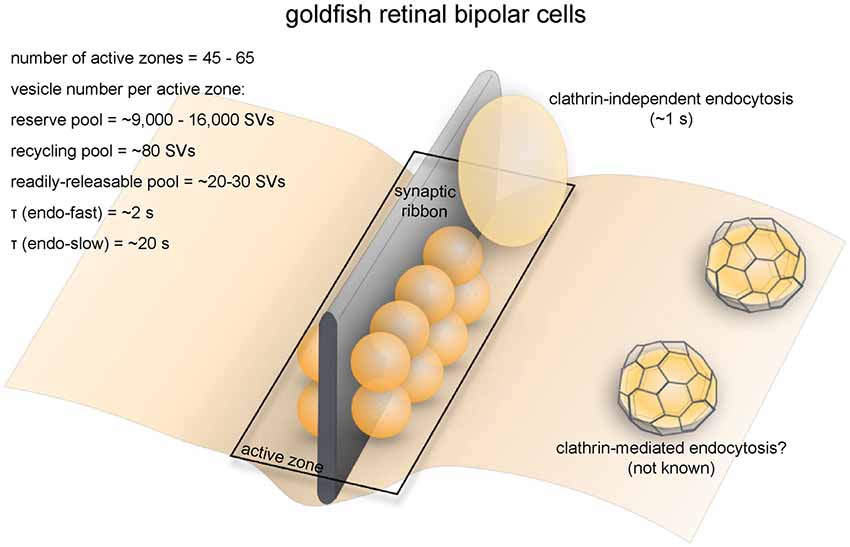
Frontiers Synaptic Vesicle Endocytosis In Different Model Systems Cellular Neuroscience

How To Fill A Synapse Science

Tj In A Neuron Synaptic Vesicles Or Neurotransmitter Vesicles Store Various Neurotransmitters That Are Released At T Neurotransmitters Neurons Neuroscience

Synaptic Vesicles Definition Neuroscientifically Challenged
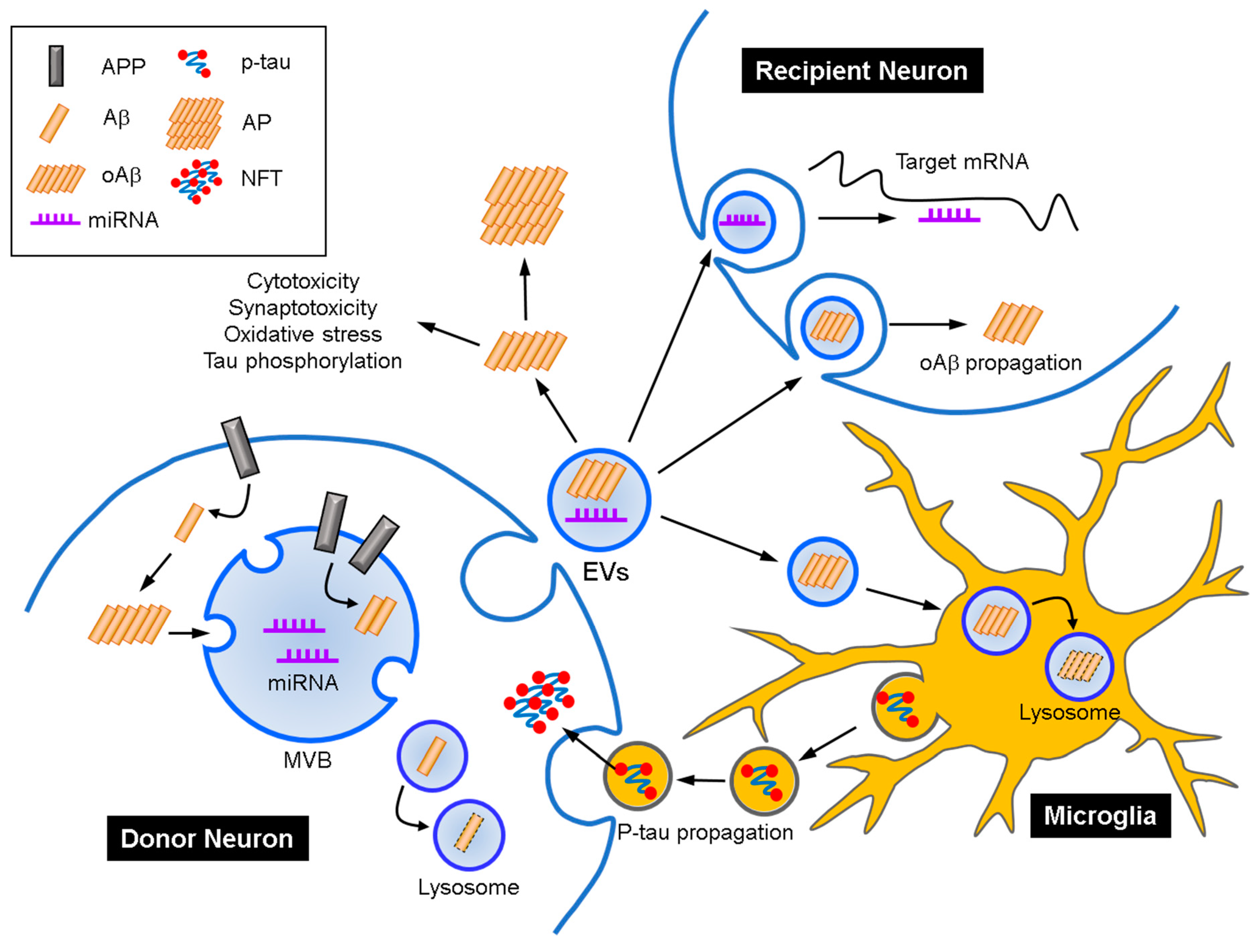
Ijms Free Full Text Extracellular Vesicle As A Source Of Alzheimer S Biomarkers Opportunities And Challenges Html

Aims Neuroscience Open Access Journals
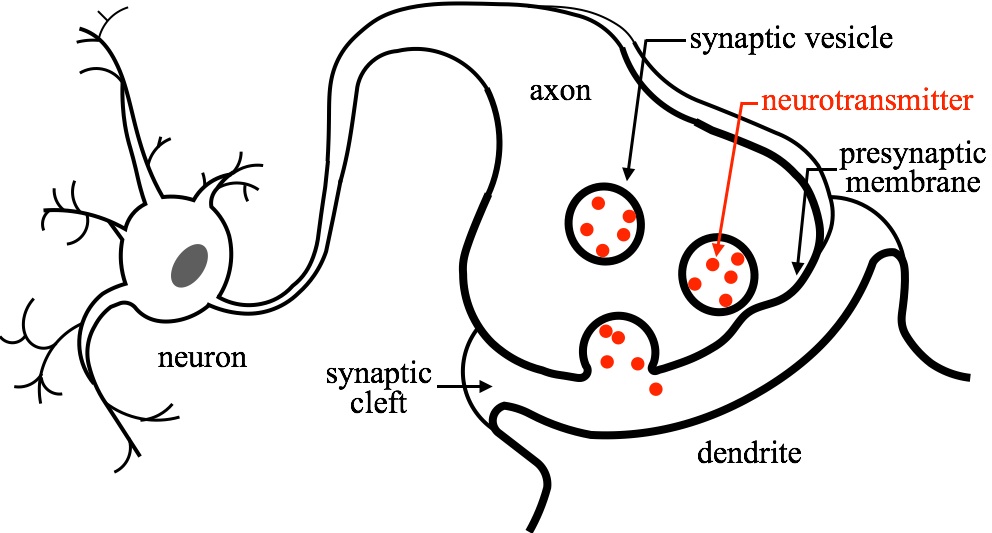
Neurotransmitter Release Regulated By Synaptotagmin I

Pin Auf Science Neuroscience
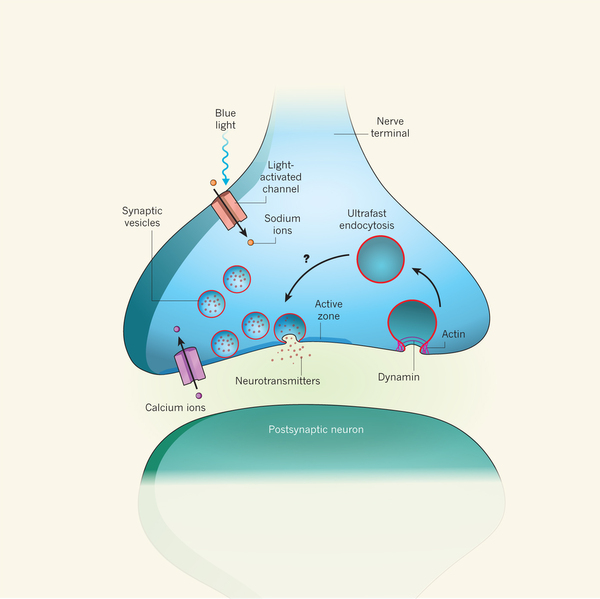
Vesicles Transport Information

Pool Size Estimations For Dense Core Vesicles In Mammalian Cns Neurons The Embo Journal

Synaptic Vesicle Fusion Is Modulated Through Feedback Inhibition By Dopamine Auto Receptors Formisano Synapse Wiley Online Library

Model Demonstrates How An Increase In Asynchronous Release And Not Download Scientific Diagram
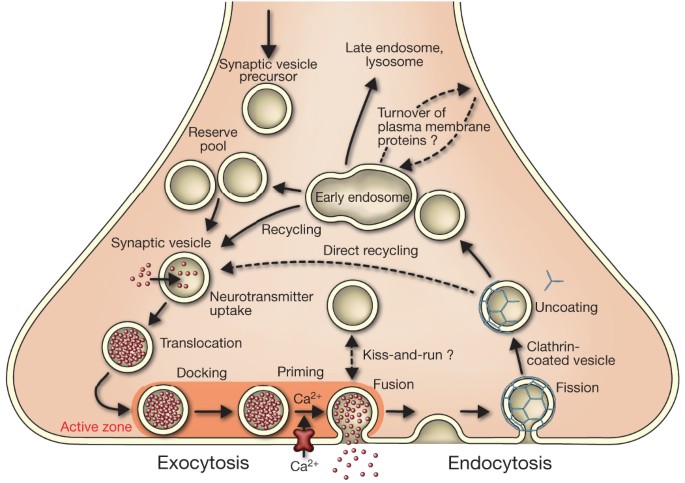
Molecular Machines Governing Exocytosis Of Synaptic Vesicles Nature

Decoding The Mystery How Do Neural Synaptic Vesicle Pools Differ Kurzweil



